Working at Height

Highlighted words reveal definitions when selected.
Falls from height are a leading cause of injury in the workplace. There are many ways a fall may be prevented; together, these controls are called fall protection.
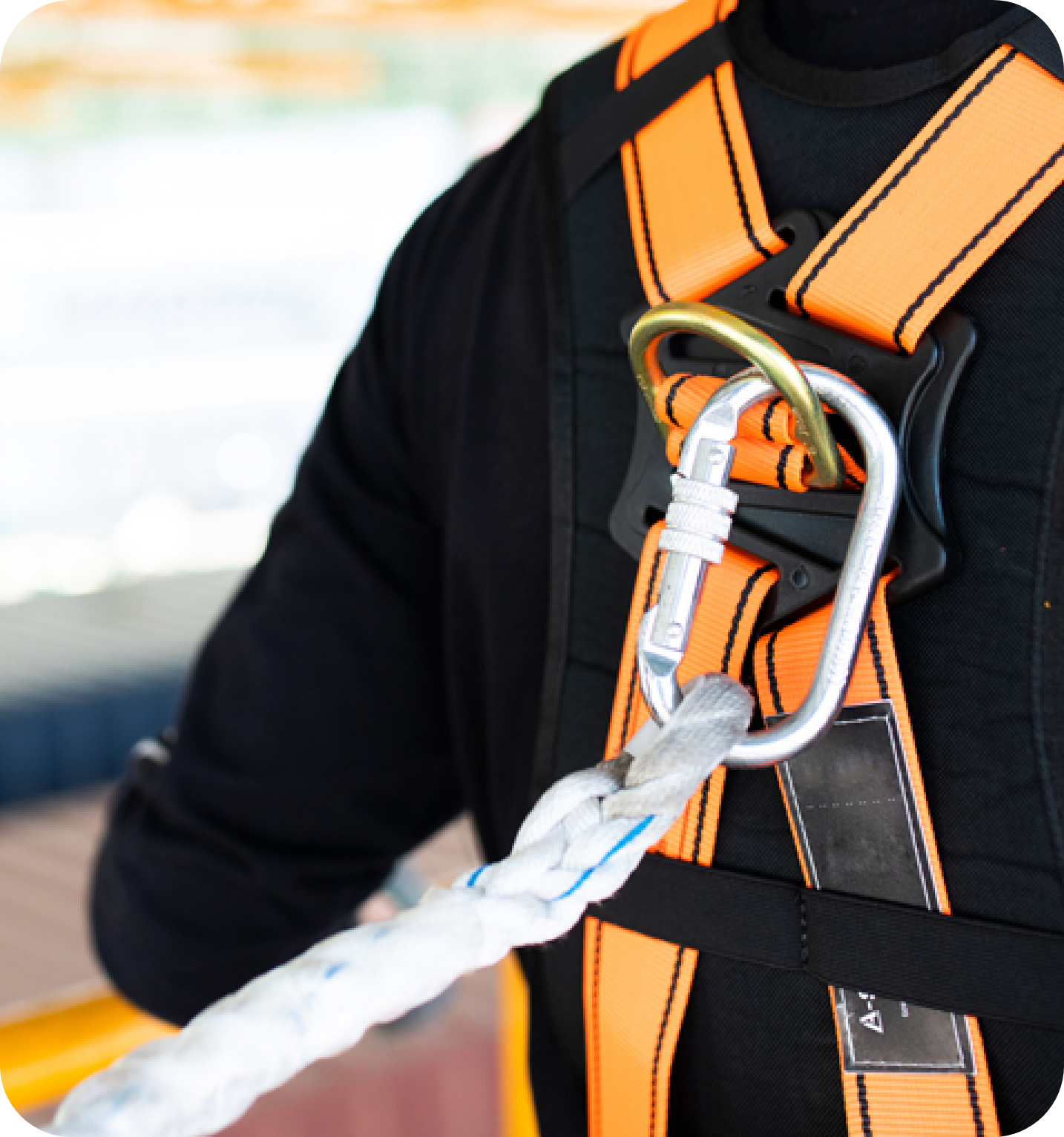
Fall protection will either prevent a fall (fall restraint), or bring the worker to a safer stop after falling (fall arrest). Fall restraint methods can vary widely from guardrails and temporary flooring to travel restraint systems. Fall arrest, on the other hand, consists of either a personal fall arrest system or safety net.
Fall protection is required for work where there is a hazard of falling: [OHS Regs., s. 141]
- Three metres or more, above a safe surface or water;
- Above a surface or thing that could cause an injury if a worker did fall; or
- Above an open tank, pit or vat that contains hazardous material.
Employer Responsibilities
Employers must:
- Have a written fall protection plan when using fall arrest or a safety net. The plan must include procedures to select, inspect, use, and maintain the equipment; and rescue a fallen worker. [OHS Regs., s. 142(10)]
- Provide workers with one or more of the following:
- Guardrails; [OHS Regs., s. 141]
- Temporary flooring; [OHS Regs., s. 141]
- A personal safety net; [OHS Regs., s. 141]
- A fall arrest that meets the requirements of the legislation;[OHS Regs., s. 141]
- Or another means of fall protection that is equal to, or greater than, the requirements of the legislation.
- Where a fall arrest system is used, the system must:
- Be inspected by a qualified person before each work shift. [OHS Regs., s. 142(5)] This inspection is the equipment user’s inspection.
- Be inspected by a qualified person, in accordance with the manufacturer’s requirements. This inspection is based on hours or conditions of use, but is typically done every 12 months.
- Not be used if it is damaged, until it is replaced or repaired. [OHS Regs., s. 142(6)(7)]
- Be removed from service, if it has been subjected to a fall or if the manufacturer's service life has elapsed.
- Not include a body belt. Body belts may only be used for fall restraint and comply with CSA Z259 Body belts and saddles for work positioning and travel restraint. [OHS Regs., s. 145]
- Make sure workers do not use fall protection equipment unless they hold a current certification in fall protection, obtained from an approved training provider. [OHS Regs., s. 139] Fall protection training expires after three years.
Guardrails
Guardrails must be installed: [OHS Regs., s. 28]
- When there is an open-sided floor, work platform, runway, walkway, or balcony that is over 1.22 metres above an existing floor, or ground;
- On walkways over open tanks that contain harmful substances, or tanks that are 1.22 metres or more in depth; and
- When there is a stairway that ends near dangerous traffic or other hazards.
Guardrails must be secured to prevent movement if it is struck by, or comes in contact with, a worker, materials, or equipment. [OHS Regs., s. 28] A guardrail must have a top rail located between 0.9 and 1.1 metres above the working surface, and an intermediate rail, located midway between the top rail and the working surface. [OHS Regs., s. 28]
Walkways and platforms installed over machinery and work areas must have toeboards at least 10 centimetres high, to prevent materials and debris from falling over the edge. [OHS Regs., s. 28(5)]
When a worker is near an open tank that contains a liquid or a harmful substance, the sides of the tank must be at least 91.44 centimetres above the working platform, or guardrails must be in place. [OHS Regs., s. 30]
Where guardrails are not practical in a vehicle service pit, the perimeter of the pit must be marked with luminescent high visibility, skid-resistant paint. The pit must also have a fixed ladder attached at each end. [OHS Regs., s. 30]
Temporary flooring
When temporary flooring is used to cover an open hole, it must be: [OHS Regs., s. 146]
- Constructed or installed at each level where work is in progress, and extending over the whole work area, except opening necessary for carrying out work;
- Extended over the whole work area, except for necessary openings;
- Able to withstand four times the maximum load it will likely have to support;
- Securely fastened to, and supported on, members that are able to withstand four times the maximum load likely to be imposed upon it; and
- Labeled to identify the hazard. [OHS Regs., s. 30]
Fall arrest
A fall arrest system must be adequately secured to an anchor point (where possible, located above the shoulder of the worker), or a lifeline that is secured to an anchor point, and must include: [OHS Regs., s. 142]
- A lanyard that complies with CSA Z259.11 Energy absorbers and lanyards;
- A energy absorber, where a person may freefall greater than 1.22 metres, that complies with CSA Z259.11 Energy absorbers and lanyards; and
- A full body harness that is adjusted to fit the user, and complies with CSA Z259.10 Full body harness.
When the fall arrest system includes a vertical lifeline, the lifeline must: [OHS Regs., s. 142(2)]
- Comply with CSA Z259.2.1 Fall arresters, vertical lifelines and rails;
- Be attached to an anchor point and be able to reach a safe surface below the work area;
- Be secured at the bottom to prevent tangling;
- Be free of knots, lubricants, splices (except where necessary to connect to the anchor point), or other imperfections;
- Be used with softeners on all sharp edges or corners;
- Be clearly identified as the lifeline, using colour or another means; and
- Include a rope grab that also complies with CSA Z259.2.1 Fall arresters, vertical lifelines and rails.
Workers must never use a lifeline that is being used by another worker, or use a rope that has been used for another purpose, such as, hoisting and rigging. [OHS Regs., s. 142(3)]
When the fall arrest system includes a static line (horizontal lifeline), it must: [OHS Regs., s. 142(8)]
- Comply with CSA Z259.13 Flexible horizontal lifeline systems and CSA Z259.16 Design of active fall protection systems;
- Have turnbuckles or similar tightening devices, at the ends of the static line;
- Have softeners at all sharp edges or corners to protect against cuts and chafing; and
- Be made only of components that are able to withstand the maximum load or 8 kilonewtons, whichever is greater.
- Be equipped with vertical supports at least every 9 metres and have a maximum deflection, when taut, of no greater than 381 mm for a 9 metre span.
When a fall arrest system is for an arborist, the system must: [OHS Regs., s. 142(9)]
- Include a tree climbing or tree trimming harness or saddle;
- Be secured to an anchor point, lifeline, or static line that is secured to an anchor point;
- Include a climbing rope or safety strap;
- Be able to withstand the maximum load or 22.2 kilonewtons, whichever is greater; and
- Where practical, include a second climbing rope or strap that:
- Provides additional stability; and
- Backup fall protection.
Safety nets
When a safety net is used, it must: [OHS Regs., s. 143]
- Be maintained so that the maximum deflection when arresting the fall of a worker does not allow a part of the worker to contact another surface;
- Have no obstructions or items a worker may strike, if they fall;
- Be installed no more than 4.6 metres below the work area;
- Extend 2.4 metres on all sides beyond the work area;
- Where connected to another personnel safety net, the splice joints connecting it with the together personnel safety nets are equal to or greater in strength than, the strength of the weakest personnel safety nets; and
- Be manufactured, used, maintained, inspected, and stored according to ANSI A10.11-1989 Safety Nets Used During Construction, Repair and Demolition Operations.
Roof work
Working from a roof is a common source of falls that often result in serious injury or death. Fall protection required for roofing depends on the pitch of the roof.
For a flat roof between 0/12 and 3/12:
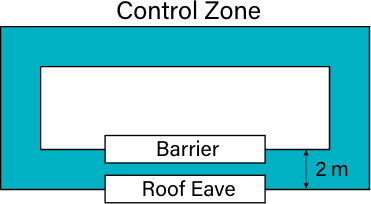
- The employer may use control zones when working on a flat roof, except for structural work, and scaffold erection and removal. The control zone must be set back a safe distance of at least two metres from the edge, with additional distance if any of the following conditions exists: [OHS Regs., s. 29]
- The working surface is slippery or sloped;
- The work is carried out at an elevation relative to the unguarded edge; or
- The risk is increased by the use of equipment near the control zone.
- Where a control zone is used, workers may only enter or leave the control zone if they are wearing fall restraint or arrest. If workers will, at all times, remain further from the unguarded edge than the width of the control zone, the use of a raised warning line or another equally effective means, is acceptable to identify the boundary of the control zone. [OHS Regs., s. 29]
For a pitched roof between 3/12 and 6/12, one of the following must be used:
- A fully decked scaffold, with toeboards installed continuously along the entire edge of the roof;
- Roof brackets, guardrails and toeboards installed along the entire edge of the eave; or
- Fall arrest. [OHS Regs., s. 141]
For a pitched roof between 6/12 and 9/12, two of the following must be used:
- A fully decked scaffold, with toeboards installed continuously along the entire edge of the roof;
- Roof brackets; or
- Fall arrest. [OHS Regs., s. 141]
When the roof pitch is greater than 9/12, roof brackets with planks, and a fall arrest system must be used. [OHS Regs., s. 29]
Dropped and falling objects
To protect workers from dropped or falling objects, consider the following controls:
- Restrict access to the area below the work, and provide adequate warning signs that state the risk of falling objects;
- Install a debris net or equal means of protection. Where debris nets are used, they must be installed no more than 4.6 metres below the work area and be manufactured, inspected, used, maintained, and stored according to ANSI A10.11-1989 Safety Nets Used During Construction, Repair and Demolition Operations; [OHS Regs., s. 144]
- Use tool lanyards to prevent accidental drops; and
- If possible, do not store materials within two metres of an edge or opening. Where this is not possible, use guardrails with toe boards.
Workers Responsibilities
Workers must:
- Take reasonable care to protect his or her health and safety and that of workers and persons at or near the workplace. [OHS Act, s. 6)]
- Properly wear or use personal protective equipment (PPE), safeguards and safety and devices provided for their protection in accordance with the manufacturer’s instructions and training provided by the employer. [OHS Act, s. 7(a)(a.1)] [OHS Regs., s. 17]
- Follow safe work practices and procedures.
- Participate in training and hazard assessments, if provided.
- Not use fall protection equipment unless you hold a current certification in fall protection obtained from an approved training provider. [OHS Regs., s. 139] Fall protection training expires after three years.
- Immediately report concerns and hazards to the supervisor or employer. [OHS Regs., s. 17(3)]
Related topics
Fall protection plan
A set of written procedures to follow when working at height, which includes requirements for rescue.Guardrails
A system of vertical and horizontal members that warns of a fall hazard and reduces the risk of a fall. [OHS Regs., s. 138]
Temporary flooring
Temporary flooring means a horizontal working surface that is designed to give access to areas that do not have permanent flooring, and will prevent a worker from falling.Safety net
A net that is used to catch a worker during a fall. [OHS Regs., s. 138]Fall arrest system
A system of physical components attached to a worker that stops a worker during a fall. [OHS Regs., s. 138]Qualified person
A person who is knowledgeable of the work, the hazards involved and the means to control the hazards, by reason of education, training, experience or a combination of them. [OHS Regs., s.2(h) and (w)]CSA
CSA is the Canadian Standards Association Group. Certain CSA standards are available for online viewing.To access these, you must first create an account with "CSA Communities".
Go to: https://community.csagroup.org/login.jspa?referer=%252Findex.jspa
Once you are logged in, click on the text below the "OHS Standards / View Access" graphic.
Click on the jurisdiction of your choice to see the CSA Standards as referenced in that legislation.
Standards may also be purchased from CSA Group: https://store.csagroup.org/
Approved training provider
Some types of training, such as confined space entry, fall protection and power line hazards, must be delivered by WorkplaceNL approved training provider. A list of approved trainers and available courses can be found in the Certification Training Registry (CTR) https://ctr.bluedrop.io/#/.Lanyard
A flexible line used to secure a worker to a lifeline, static line, or a fixed anchor point.[OHS Regs., s. 138]
Shock absorber
In a personal fall arrest system, an energy (shock) absorber is a device designed to reduce the force placed on the body and the fall arrest system components, in the event of a fall.Energy absorbers are required in a system when free fall of over 1.22 metres (4 feet). [OHS Regs., s. 142(1)(c)]
Full body harness
A harness consisting of leg and shoulder straps and an upper back suspension unit that distributes and reduces the impact force of a fall. [OHS Regs., s. 138]Vertical lifeline
A vertical line attached to a fixed anchor point or a static line and to which a lanyard and a ropegrab may be attached. [OHS Regs., s. 138]Softeners
Padding or hoses that are used with a lifeline or static line to prevent a rope from being cut or chafed. [OHS Regs., s. 138]Rope grab
A mechanical fall-arrest device that is attached to a lifeline and a lanyard, and locks itself immediately on the lifeline in the event of a fall. [OHS Regs., s. 138]Static line
A horizontal lifeline that is attached horizontally to two or more fixed anchor points, and to which a fall arrest system is attached. [OHS Regs., s. 138]Turnbuckles
A device located at both ends of a static (horizontal) lifeline which regulates the length and tension of the lifeline.Arborist
A worker trained and employed, in whole or in part, to climb trees for an economic or scientific purpose, including:- Detection and treatment of disease, infections or infestations,
- Pruning, spraying or trimming,
- Repairing damaged trees,
- Assessing growth or harvesting potential, or
- Scientific research. [OHS Regs., s. 138]
Saddle
A tree trimming saddle is a type of harness that consists of nylon straps that fit securely around the climber's waist and thighs. The harness ensures the safety of the climber if they should fall.Climbing rope or safety strap
A rope or strap used for tree climbing.ANSI
ANSI is the American National Standards Institute.Standards may be purchased from the ANSI store: https://webstore.ansi.org/
Pitch
Pitch or steepness is defined as the vertical rise over the horizontal run.
Control zone when working on a flat roof
Control zone means the area between an unguarded edge of a building or structure and a line.The control zone method of fall protection is intended for level or low-sloped work surfaces. It is not to be used on a working surface where the slope of that surface exceeds 3/12 horizontal, or for skeletal structure work or scaffold erection and removal.
Raised warning line
When using a control zone, a raised warning line includes a line:- Of high-visibility material, or a line flagged or clearly marked with high visibility materials at intervals not exceeding 2 metres;
- Rigged and maintained to be between 0.85 metres and 1.15 metres above the working surface; and
- that is easily detected when a worker touches it
Scaffold or scaffolding
Scaffold or scaffolding means a temporary work platform and its supporting structure used for supporting workers or materials or both. [OHS Regs., s. 157]Roof bracket
Roof bracket a term commonly used to describe devices, normally of metal construction, that are attached to a sloped roof to support and secure planks that are needed to provide secure footing for workers.Debris net
A net that is used to catch material and debris that can drop from work areas overhead. [OHS Regs., s. 138]Tool lanyards
A tool lanyard is a device designed to reduce the risk of a dropped tool by securely attaching the tool to the worker.OCCUPATIONAL HEALTH AND SAFETY ACT
R.S.N.L. 1990, c. O-3
Section 6 Workers' general duty
6. A worker, while at work, shall take reasonable care to protect his or her own health and safety and that of workers and other persons at or near the workplace.
Section 7 Specific duties of workers
7. A worker
(a) shall co-operate with his or her employer and with other workers in the workplace to protect
(i) his or her own health and safety,
(ii) the health and safety of other workers engaged in the work of the employer,
(iii) the health and safety of other workers or persons not engaged in the work of the employer but present at or near the workplace;
(a.1) shall use devices and equipment provided for his or her protection in accordance with the instructions for use and training provided with respect to the devices and equipment;
(b) shall consult and co-operate with the occupational health and safety committee, the worker health and safety representative or the workplace health and safety designate at the workplace; and
(c) shall co-operate with a person exercising a duty imposed by this Act or regulations.
[S.N.L. 1999, c. 28, s. 3; 2001, c. 10, s. 26; 2004, c. 52, s. 2]
Occupational Health and Safety Regulations, 2012
N.L.R. 5/12
Part I GENERAL
Section 2 Interpretation
2. (1) In these regulations
(a) "accident" includes
(i) an event occasioned by a physical or natural cause, or
(ii) disablement arising out of and in the course of employment;
(b) "ACGIH" means the American Conference of Governmental Industrial Hygienists;
(c) "Act" means the Occupational Health and Safety Act ;
(d) "administrative controls" means the provision, use and scheduling of work activities and resources in the workplace, including planning, organizing, staffing and coordinating, for the purpose of controlling risk;
(e) "ASHRAE" means the American Society of Heating, Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Engineers;
(f) "authorized" means, in reference to a person, a qualified person designated by an employer to carry out specific functions;
(g) "commission" means the Workplace Health, Safety and Compensation Commission continued under the Workplace Health, Safety and Compensation Act, 2022 ;
(h) "competent" means a person who is
(i) qualified because of that person's knowledge, training and experience to do the assigned work in a manner that ensures the health and safety of every person in the workplace, and
(ii) knowledgeable about the provisions of the Act and these regulations that apply to the assigned work, and about potential or actual danger to health or safety associated with the assigned work;
(i) "construction" means building, erection, excavation, alteration, repair, renovation, dismantling, demolition, structural maintenance, painting, moving, land clearing, earth moving, grading, street and highway building, concreting, equipment installation and alteration and the structural installation of construction components and materials in any form or for any purpose, and work in connection with it;
(j) "CSA" means the Canadian Standards Association;
(k) "engineering controls" means the physical arrangement, design or alteration of workstations, equipment, materials, production facilities or other aspects of the physical work environment, for the purpose of controlling risk;
(l) "hazardous health occupation" means an occupation from which an occupational disease may arise;
(m) "hot work" means work which involves burning, welding, cutting, grinding, using fire or spark producing tools or other work that produces a source of ignition;
(n) "injury" means
(i) an injury as a result of a chance event occasioned by a physical or natural cause, (ii) an injury as a result of wilful and intentional act, not being the act of the worker, (iii) disablement, (iv) occupational disease, or (v) death as a result of an injury arising out of and in the course of employment and includes a recurrence of an injury and an aggravation of a pre-existing condition but does not include stress other than stress that is an acute reaction to a sudden and unexpected traumatic event;
(o) "ISO" means the International Organization for Standardization;
(p) "mine" means mine as defined in the Mining Act ;
(q) "occupation" means an employment, business, calling or pursuit but does not include an endeavour that is not included in one of the classes of occupations in the current National Occupational Classification List developed by the Department of Human Resources and Social Development Canada in collaboration with Statistics Canada;
(r) "occupational disease" means a disease prescribed by regulations under the Workplace Health, Safety and Compensation Act and another disease peculiar to or characteristic of a particular industrial process, trade or occupation;
(s) "occupational health service" means a service established in or near a workplace to maintain and promote the physical and mental well-being of workers and may include personnel, equipment, transportation, supplies and facilities;
(t) "plant" means buildings, equipment and facilities where a worker or self-employed person is engaged in an occupation;
(u) "professional engineer" means a person who holds a certificate of registration to engage in the practice of engineering under the Engineers and Geoscientists Act;
(v) "proof test" means a test applied to a product to determine material or manufacturing defects;
(w) "qualified" means being knowledgeable of the work, the hazards involved and the means to control the hazards, by reason of education, training, experience or a combination of them;
(x) "TLV" means the documentation of threshold limit values for chemical substances and physical agents in the work environment published annually or more frequently by the ACGIH; and
(y) "work platform" means an elevated or suspended temporary work base for workers.
(2) In these regulations, a reference to a code or guideline, unless otherwise stated, includes amendments to that code or guideline and a reference shall be presumed to be a reference to the most current code or guideline.
(3) Where there is a conflict between a standard established by these regulations or a code or standard adopted by these regulations, the more stringent standard applies.
[S.N.L. 2022, c. W-11.1, s. 168]
Part III GENERAL DUTIES
Section 17 General duties of workers
17. (1) A worker shall make proper use of all necessary safeguards, protective clothing, safety devices, lifting devices or aids, and appliances
(a) designated and provided for the worker’s protection by the employer; or
(b) required under these regulations to be used or worn by a worker.
(2) A worker shall follow the safe work procedure in which the worker has been instructed.
(3) A worker shall immediately report a hazardous work condition that may come to the worker’s attention to the employer or supervisor.
[N.L.R. 43/22, s. 4]
Part V GENERAL HEALTH AND SAFETY REQUIREMENTS
Section 28 Guardrails
28. (1) Guardrails shall be installed where an open-sided floor, working platform, runway, walkway or balcony is over 1.22 metres above the existing floor or ground level.
(2) Detour guardrails shall be installed where a stairway ends in direct proximity to dangerous traffic or other hazards.
(3) An employer shall ensure that a guardrail is secured so that it cannot move in any direction if it is struck or if a point on it comes in contact with a worker, materials or equipment.
(4) Guardrails shall be installed on walkways over open tanks containing harmful substances or over open tanks 1.22 metres or more in depth.
(5) Walkways and platforms installed over machinery and work areas shall be equipped with toe boards at least 10 centimetres high along all sides of the walkway or platform.
(6) A guard rail shall have a top rail located at least .9 metres but not more than 1.1 metres above the working surface and an intermediate rail located midway between the top rail and the working surface.
Section 29 Roof work
29. (1) Where work is being done at a distance greater than 2 metres from the edge of a roof that has a slope of less than 3/12, the employer shall implement control zones to alert workers upon entering within 2 metres of the edge without an appropriate means of fall protection.
(2) Where work is being done from the edge of a roof or within 2 metres of the edge of a roof that has a slope of less than 3/12 in circumstances described in paragraph 141(a), (b) or (c), fall protection shall be used, in accordance with paragraph 141(d), (e), (f), (g), or (h).
(3) Where work is being done from or on a roof that has a slope that is equal to or greater than 3/12 but less than 6/12, under circumstances described in paragraph 141(a), (b) or (c)
(a) a fully decked scaffold with toeboards installed continuously along the edge of the roof,
(b) roof brackets, guardrails and toeboards installed continuously along the edge of the roof, or
(c) a fall arrest system in accordance with paragraph 141(d)
shall be implemented.
(4) Where work is being done from a roof that has a slope that is equal to or greater than 6/12 but less than 9/12, under circumstances described in paragraph 141(a), (b) or (c), a combination of 2 of the following shall be implemented:
(a) roof brackets,
(b) a fully decked scaffold with toeboards installed continuously along the length of the eave, and
(c) a fall arrest system in accordance with paragraph 141(d).
(5) Where work is done from or on a roof that has a slope equal to or greater than 9/12, under circumstances described in paragraph 141(a), (b) or (c), roof brackets with planks and a fall arrest system shall be used in accordance with these regulations.
(6) Crawl boards and ladders used for roof work shall be securely fastened over the ridge of the roof or be otherwise effectively anchored.
(7) An eavestrough shall not be used to support a crawl board or ladder on a roof.
Section 30 Openings, pits and tanks
30. (1) Where a worker is employed around an open tank containing liquid or a harmful substance, the sides of the tanks shall be constructed to extend at least 91.44 centimetres above a working platform or standard guardrails shall be provided to prevent the worker from falling into the tank.
(2) A hole or pit in a floor, roof, walkway or work area accessible to a worker shall be securely covered and identified.
(3) Where a vehicle service pit is used so frequently that compliance with this section is impractical, the perimeter of the pit shall be delineated by high visibility, luminescent, skid-resistant paint instead of guardrails.
(4) A vehicle service pit shall have a fixed ladder at each end.
Part X FALL PROTECTION
Section 138 Definitions
138. In this Part
(a) "anchorage point" means a secure point of attachment for a lifeline or lanyard;
(b) "arborist" means a worker trained and employed, in whole or in part, to climb trees for an economic or scientific purpose, including
(i) detection and treatment of disease, infections or infestations,
(ii) pruning, spraying or trimming,
(iii) repairing damaged trees,
(iv) assessing growth or harvesting potential, or
(v) scientific research;
(c) "body belt" means a belt worn by a worker as a means of fall restraint;
(d) "debris net" means a net that is used to catch material and debris that can drop from work areas;
(e) "fall arrest system" means a system of physical components attached to a worker that stops a worker during a fall;
(f) "full body harness" means a harness consisting of leg and shoulder straps and an upper back suspension unit that distributes and reduces the impact force of a fall;
(g) "guardrail" means a system of vertical and horizontal members that warns of a fall hazard and reduces the risk of a fall;
(h) "lanyard" means a flexible line used to secure a worker to a lifeline, a static line or a fixed anchor point;
(i) "lifeline" means a vertical line attached to a fixed anchor point or a static line and to which a lanyard and a ropegrab may be attached;
(j) "means of fall protection" means a fall protection system and includes a harness, net, rope, body belt, structure or other equipment or device or means of
(i) restraining a worker who is at risk of falling, or
(ii) stopping a worker who has fallen;
(k) "personnel safety net" means a net that is used to catch a worker during a fall;
(l) "ropegrab" means a mechanical fall-arrest device that
(i) is attached to a lifeline and a lanyard, and
(ii) locks itself immediately on the lifeline in the event of a fall;
(m) "safe surface" means a surface at a workplace that
(i) has sufficient size and strength to adequately support a worker who falls on to the surface, and
(ii) is sufficiently horizontal to prevent a further fall from the surface by a worker who has fallen on to the surface;
(n) "softener" means padding or hoses that are used with a lifeline or static line to prevent a rope from being cut or chafed; and
(o) "static line" or "horizontal life line" means a rope
(i) that is attached horizontally to 2 or more fixed anchor points, and
(ii) to which a fall arrest system is attached.
Section 139 Training requirement
139. A worker shall not use fall protection equipment after January 1, 2012 unless the worker has completed a training program on fall protection prescribed by the commission.
[N.L.R. 43/22, s. 23]
Section 141 General requirements
141. Where a worker is exposed to the hazard of falling from a work area that is
(a) 3 metres or more above the nearest safe surface or water;
(b) above a surface or thing that could cause injury to the worker if the worker were to fall on the surface or thing; or
(c) above an open tank, pit or vat containing hazardous material,
the employer shall ensure that
(d) the worker is provided with a fall arrest system that meets the requirements of section 142;
(e) a guardrail that meets the requirements of section 28 is constructed or installed at the work area;
(f) a personnel safety net that meets the requirements of section 143 is installed at the work area;
(g) temporary flooring that meets the requirements of section 146 is constructed or installed at the work area; or
(h) the worker is provided with another means of fall protection that provides a level of safety equal to or greater than a fall arrest system that meets the requirements of section 142.
Section 142 Fall arrest system
142. (1) A fall arrest system that is provided in accordance with section 141 shall
(a) be adequately secured to
(i) an anchorage point, or
(ii) that complies with
(A) CSA Standard Z259.11 "Personal Energy Absorbers and Lanyards", or
(B) CSA Standard Z259.2.2 "Self-Retracting Devices".
(b) include a lanyard
(i) that is attached to an anchorage point or lifeline, where practicable, above the shoulder of the worker, and
(ii) that complies with CSA Standard Z259.11 "Energy Absorbers and Lanyards ";
(c) prevent a free fall greater than 1.22 metres where
(i) the fall arrest system is not equipped with a shock absorption system that complies with CSA Standard Z259.11 Personal Energy Absorbers and Lanyards and that reduces the shock level of a fall to less than 4 kilonewtons, or
(ii) the combined free fall and shock absorbed deceleration distance exceeds the distance between the work area and a safe surface;
(d) include a full body harness that
(i) is attached to a lanyard,
(ii) is adjusted to fit the user of the harness, and
(iii) complies with CSA Standard Z259.10 "Full Body Harnesses" ; and
(e) include connecting components that comply with CSA Standard Z259.12 "Connecting Components for Personal Fall Arrest Systems".
(2) Where a fall arrest system includes a lifeline, the lifeline shall
(a) comply with CSA Standard Z259.2.5 "Fall Arresters and Vertical Lifelines";
(b) extend to a safe surface below the work area and be securely attached to an anchorage point;
(c) be secured at the bottom of the lifeline to prevent tangling or disturbance of the line and be free of knots, lubricants and imperfections;
(d) be free of splices, except where they are necessary to connect the lifeline to an anchorage point;
(e) be provided with softeners at all sharp edges or corners to protect against cuts or chafing; and
(f) be clearly identified as a lifeline by colour or by another means that provides an equivalent level of safety.
(3) No worker shall
(a) use a lifeline in a fall arrest system while that fall arrest system is being used by another worker; or
(b) provide a rope for use, or permit a rope to be used, as a lifeline in a fall arrest system where the rope has been used for another purpose.
(4) Where a fall arrest system provided to a worker includes a ropegrab, the ropegrab used shall comply with
(a) CSA Standard Z259.2.4 "Fall Arresters and Vertical Rigid Rails"; and
(b) CSA Standard Z259.2.5 "Fall Arresters and Vertical Lifelines".
(5) An employer who provides a worker with a fall arrest system shall ensure the fall arrest system is inspected by a qualified person before each work shift undertaken by the worker.
(6) A qualified person who carries out an inspection of a fall arrest system shall advise the employer where a component of the system is defective in condition or function and the employer shall ensure that the system is not used until the defective component is replaced or repaired.
(7) Where a fall arrest system has arrested the fall of a worker at a work area, the employer shall ensure that the fall arrest system
(a) is removed from service and inspected by a qualified person; and
(b) is repaired, before it is reused, to the original manufacturer's specifications, where an inspection under paragraph (a) reveals that a component of the system is defective.
(8) Where a fall arrest system includes a static line, the static line shall
(a) have a nominal diameter of at least 12.7 millimetres and be made of improved plow wire rope;
(b) be equipped with vertical supports at least every 9 metres and have a maximum deflection, when taut, of no greater than 381 millimetres for a 9 metre span;
(c) be equipped with turnbuckles or other comparable tightening devices that provide an equivalent level of protection, at the ends of the static line;
(d) be equipped with softeners at all sharp edges or corners to protect against cuts or chafing;
(e) be made only of components that are able to withstand either the maximum load likely to be imposed on the components or a load of 8 kilonewtons, whichever is the greater; and
(f) comply with CSA Standard Z259.13 "Flexible Horizontal Lifeline Systems" and CSA Standard Z259.16 "Design of Active Fall Protection Systems".
(9) Where a fall arrest system is provided to an arborist, the fall arrest system shall
(a) include a tree climbing or tree trimming harness or saddle;
(b) be adequately secured to
(i) an anchorage point, or
(ii) a lifeline that is
(A) securely fastened to anchorage points, or
(B) attached to a static line that is securely fastened to anchorage points;
(c) include a climbing rope or safety strap;
(d) where practicable, include a second climbing rope or safety strap that
(i) provides additional stability, and
(ii) back-up fall protection; and
(e) be capable of withstanding either the maximum load likely to be imposed or a load of 22.2 kilonewtons, whichever is the greater.
(10) Where an employer uses a fall arrest system or a personnel safety net as a means of fall protection, the employer shall have a written fall protection plan that specifies
(a) the procedure to assemble, maintain, inspect, use and disassemble the fall arrest system or personnel safety net; and
(b) the procedure for the rescue of a worker who has fallen and is suspended by the fall arrest system or personnel safety net, but is unable to effect self-rescue.
[N.L.R. 43/22, s. 24]
Section 143 Nets
143. (1) Where a personnel safety net is installed in accordance with section 141, an employer shall ensure that it
(a) is installed
(i) not more than 4.6 metres below the work area,
(ii) to ensure that no obstructions or intervening members may be struck by a worker during a fall between the work area and the personnel safety net, and
(iii) maintained so that the maximum deflection when arresting the fall of a worker does not allow a part of the worker to contact another surface;
(b) extends 2.4 metres on all sides beyond the work area; and
(c) where connected to another personnel safety net, the splice joints connecting it with the other personnel safety nets are equal to, or greater in strength than, the strength of the weakest of the personnel safety nets.
(2) Notwithstanding subsection (1), an employer shall ensure that a personnel safety net is manufactured, used, maintained, inspected and stored in accordance with ANSI Standard A10.11-1989 "Safety Nets Used During Construction, Repair and Demolition Operations".
Section 144 Debris nets
144. (1) Where a worker having access to an area below an elevated work area is exposed to the hazard of falling objects or debris from the work area, an employer shall ensure that
(a) a debris net is installed below the work area in accordance with subsection (2); or
(b) other means of protection are provided that provide an equivalent level of protection from falling objects and debris.
(2) An employer shall ensure that a debris net under subsection (1) is
(a) manufactured, used, maintained, inspected and stored in accordance with ANSI Standard A10.11-1989 "Safety Nets Used during Construction, Repair and Demolition Operations"; and
(b) installed not more than 4.6 metres below the elevated work area.
Section 145 Travel restraint
145. An employer shall ensure that a body belt provided in accordance with section 141 complies with CSA Standard Z259 "Body Belts and Saddles for Work Positioning and Travel Restraint".
Section 146 Temporary flooring
146. Temporary flooring that is constructed or installed in accordance with section 141 shall
(a) be constructed or installed at each floor level of the work area where work is in progress;
(b) extend over the whole work area except for openings necessary for the carrying out of work;
(c) be able to withstand 4 times the maximum load likely to be imposed on it; and
(d) be securely fastened to and supported on members that are able to withstand 4 times the maximum load likely to be imposed on them.
Part XI SCAFFOLDS, STAGES AND WORK PLATFORMS
Section 157 Definitions
157. For the purpose of this section and sections 158 to 200,
(a) "building tie" means a connection between a standing scaffold and a permanent structure;
(b) "double-pole scaffold" means a scaffold with both ends of the bearers supported by connections to posts or uprights;
(c) "heavy duty" means intended to support both workers and stored or stacked materials, including bricks and masonry, where the maximum load capacity does not exceed 366 kilograms a square metre;
(d) "light duty" means intended to support workers, their personal hand tools and material for immediate use only where the maximum load capacity does not exceed 122 kilograms a square metre;
(e) "painter's plank" means a single manufactured extension staging;
(f) "running scaffold" means a double-pole scaffold comprised of 2 or more bays;
(g) "scaffold" or "scaffolding" means a temporary work platform and its supporting structure used for supporting workers or materials or both; and
(h) "single pole scaffold" means a scaffold with the outer ends of the bearers supported on ledgers secured to a single row of posts or uprights, and the inner ends of the bearers supported on or in a wall.
CCOHS



