Elevating Work Platforms
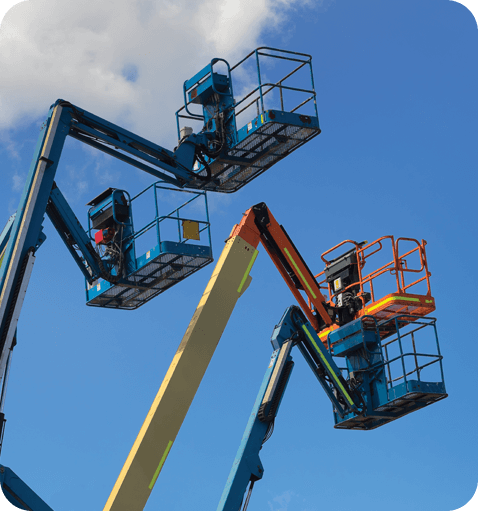
Highlighted words reveal definitions when selected.
Elevating work platforms are devices used to lift and position a worker above ground level. They are also called aerial work platforms or lifts. Some common types include scissor lift, booms and aerial devices. They may be vehicle-mounted or self-propelled. They may be telescoping, articulating, or both.
Elevating work platforms must be inspected, maintained, modified, repaired, and operated in accordance with the manufacturer’s instructions, applicable standards and legislation. Operators must be properly trained to operate the equipment and may require additional training for protection from hazards, like falls and powerlines.
Employer Responsibilities
Employers must:
- Make all reasonable efforts to protect the health, safety and welfare of their workers. [OHS Act, s. 4]
- Provide and maintain a workplace and the necessary equipment, systems, and tools in a manner that is safe and without risk to workers. [OHS Act, s. 5(a)]
- Provide the necessary information, instruction, training, supervision, and facilities. [OHS Act, s. 5(b)]
- Make sure necessary personal protective equipment (PPE) and devices are used. [OHS Regs., s. 14(2)]
- Make sure that operators and occupants of an elevating work platform are trained in accordance with the relevant CSA Standards below, including refresher training. Operators must carry proof if training on their person. [OHS Regs., s. 202]
- CSA Standard CAN/CSA B354.4 "Self-propelled Boom-Supported Elevating Work Platforms”.
- ANSI Standard ANSI /SIA A92.5 "Boom-Supported Elevating Work Platforms".
- CSA Standard CAN/CSA B354.2 "Self-Propelled Elevating Work Platforms".
- ANSI Standard ANSI /SIA A92.6 "American National Standard for Self-Propelled Elevating Work Platforms".
- CSA Standard CAN/CSA B354.1 "Portable Elevating Work Platforms".
- ANSI Standard ANSI /SIA A92.3 "American National Standard for Manually Propelled Elevating Aerial Platforms”.
- CSA Standard CAN/CSA C225 "Vehicle-Mounted Aerial Devices".
- Make sure workers do not use fall protection equipment unless they hold a current certification in fall protection, obtained from an approved training provider. Fall protection training expires after three years. [OHS Regs., s. 139]
- Make sure workers who wear PPE are adequately instructed in their correct use, limitations, and assigned maintenance duties. [OHS Regs., s. 72]
- Make sure that safe work procedures are followed and that safe work procedures promote the safe interaction of workers and their work environment. [OHS Regs., s. 14(3) and (4)]
- Conduct a risk assessment in a workplace where a need to rescue or evacuate workers may arise. When the risk assessment identifies a need for evacuation or rescue, develop written rescue and evacuation procedures and assign a worker to coordinate their implementation. Written rescue and evacuation procedures are required for work at height. [OHS Regs., s. 38]
- Cylindrical objects (e.g., compressed or liquefied gas cylinders, fire extinguishers, etc.) transported on their sides are restrained to prevent unintended movement. [OHS Regs., s. 276]
Loading
When using an elevating work platform, the employer must make sure:
- Operators follow the safe working load (SWL) specified by the manufacturer, unless instructed otherwise by legislation. [OHS Regs., s. 16(1)]
- The SWL is certified by a professional engineer, or another person acceptable to OHS Division, when: [OHS Regs., s. 16(2)]
- The manufacturer’s specifications or warranty cannot be provided;
- The equipment has been modified in a way that changes its SWL;
- Wear, corrosion, damage, or signs of fatigue are found that may affect the SWL;
- The equipment is used in a way or for a purpose other than what it was designed for that changes the SWL; or
- An OHS Officer considers certification necessary.
- An elevating work platform has permanent marking indicating the SWL, which can be easily seen and read by the operator. [OHS Regs., s. 259]
- Cylindrical objects (e.g., compressed or liquefied gas cylinders, fire extinguishers, etc.) transported on their sides are restrained to prevent unintended movement. [OHS Regs., s. 276]
- Unitized loads do not project a distance greater than half its height above the fork carriage, back rest, or back rest extension of the lift truck. [OHS Regs., s. 277(1)]
- Loose objects that are part of the load do not project above the fork carriage, back rest, or back extension of a lift truck. [OHS Regs., s. 277(2)]
- Loads that may shift during transportation are restrained if shifting could result in the instability of the load or the lift truck. [OHS Regs., s. 277(3)]
Inspect, repair, maintain, modify, and operate
Where elevating work platforms are used, the employer must:
- Inspect the elevating work platform at appropriate intervals and in accordance with the manufacturer’s instructions to maintain safe working conditions and correct unsafe conditions. If emergency action is required to correct a condition, only qualified persons may be exposed to the hazard, and every effort must be made to control the hazard while it is being corrected. [OHS Regs., s. 18]
- Make sure an elevating work platform is capable of safely performing the functions for which it is used, and that it is selected, used, and operated according to the manufacturer’s instructions, applicable standards and legislation. [OHS Regs., s. 88]
- Make sure a self-propelled work platform that has a boom-supported elevating platform which telescopes, articulates, rotates, or extends beyond the base dimensions, and is not mounted on a separate self-propelled vehicle meets the requirements of CSA Standard CAN/CSA-B354.4 “Self-propelled boom-supported elevating work platforms”, ANSI Standard ANSI/SIA A92.5 “Boom-Supported Elevating Work Platforms” or another standard acceptable to OHS Division. [OHS Regs., s. 202]
- Make sure a self-propelled integral chassis elevating work platform that has a platform that cannot be positioned laterally completely beyond the base and has primary functions controlled from the platform meets the requirements of CSA Standard CAN/CSA-B354.2 “Self-propelled elevating work platforms”, ANSI Standard ANSI/SIA A92.6 “American National Standard for Self-Propelled Elevating Work Platforms”, or another standard acceptable to OHS Division. [OHS Regs., s. 202]
- Make sure a manually propelled, integral chassis elevating work platform that has a platform that cannot be positioned laterally completely beyond the base, which may be adjusted by manual or powered means and which must not be occupied when moved horizontally, meets the requirements of CSA Standard CAN/CSA-B354.1 “Portable elevating work platforms”, ANSI Standard ANSI/SIA A92.3 “American National Standard for Manually Propelled Elevating Aerial Platforms”, or another standard acceptable to OHS Division. [OHS Regs., s. 202]
- Make sure a vehicle mounted telescopic aerial device, aerial ladder, articulating aerial device, vertical tower, material-lifting aerial device or a combination of these meets the requirements of CSA Standard CAN/CSA-C225 “Vehicle-mounted aerial devices” or another standard acceptable to OHS Division. If the type of elevated work platform is not mentioned above, it must meet a standard acceptable to OHS Division. [OHS Regs., s. 202]
- Make sure a person on an elevating work platform wears a personal fall arrest system secured to an anchorage point that is approved by the manufacturer or professional engineer. [OHS Regs., s. 207(1)]
- Make sure a worker on an aerial ladder is continuously protected by a personal fall arrest system or maintains three points of contact with the ladder at all times. [OHS Regs., s. 207(2)]
- Maintain elevating work platform in a safe operating condition. [OHS Regs., s. 251]
- Make sure the manufacturer's operation manual and maintenance manual are available at the workplace. The maintenance manual must include maintenance instructions and replacement part information. Where the manual is not available, the equipment must not be used until the manual is present or until written instructions are supplied by a professional engineer. [OHS Regs., s. 203]
- Make sure records of inspection, maintenance, repair, and modification are kept by the operator and a person responsible for inspecting and maintaining the equipment. Where these records are not available, a professional engineer must inspect and certify the elevation work platform before use, and an inspection and maintenance recording system must be established. [OHS Regs., s. 204]
- Inspect, maintain, repair, and modify an elevated work platform in accordance with the manufacturer's instructions, a relevant CSA standard, under the direction of a professional engineer, or in accordance with another standard acceptable to OHS Division. [OHS Regs., s. 206(1)]
- Make sure an insulated aerial device is dielectrically tested at least annually according to CSA Standard CAN/CSA-C225 “Vehicle mounted aerial devices” or another standard acceptable to OHS Division. The insulating capability of the aerial device must be certified by the testing agency. [OHS Regs., s. 206(2)]
- Provide a safe means for workers to get on and off the platform. [OHS Regs., s. 208]
- Make sure the rated capacity is marked on the platform and make sure the capacity is not exceeded. [OHS Regs., s. 209]
- Make sure outriggers are used according to the manufacturer's instructions. Clearly display at the operating controls, notices indicating the circumstances for which the outriggers are to be used as specified by the manufacturer. [OHS Regs., s. 210]
- Make sure controls are: [OHS Regs., s. 211]
- Clearly identified to indicate their function
- A 'hold-to-run' (continuous pressure) type that returns to the neutral or stop position when released.
- Protected against unintentional operation.
- Provided with an emergency stop device. An emergency stop device must be within easy reach of the operator, clearly labelled 'STOP', and red in colour.
- Provide a clearly marked overriding lowering control to allow a worker at the lower controls to stop and lower the platform in an emergency. [OHS Regs., s. 211(6)]
- Secure carrier vehicles of an elevated work platform against inadvertent movement before a worker occupies the platform. [OHS Regs., s. 212(1)]
- Secure a vehicle's wheels according to the manufacturer's instructions, where work is to be done on sloping ground. Where no instructions have been provided the wheels must be chocked. [OHS Regs., s. 212(2)]
- Adequately guard or identify with signs, decals or similar markings an elevating work platform lifting mechanism which creates a shear hazard to workers. [OHS Regs., s. 213]
- Equip an elevating work platform with a warning system that has an intermittent horn and flashing light which is automatically activated during motion of the work platform. The only exception are vehicle-mounted aerial devices which comply with the requirements of CSA Standard CAN/CSA-C225 “Vehicle mounted aerial device”. [OHS Regs., s. 214]
- Not permit workers to be transported on an elevated work platform, unless transportation is done according to the manufacturer's instructions. [OHS Regs., s. 215]
- Make sure that window cleaning operations are done according to the requirements of CSA Standard CAN/CSA-Z91 "Health and safety code for suspended equipment operations" or another standard acceptable to OHS Division. [OHS Regs., s. 249]
Suspended work platforms
Where a work platform is suspended by a crane or hoist, the employer must make sure:
- Each occupant uses a personal fall arrest system with a shock absorbing lanyard secured to a designated anchorage point on the platform or above the load hook. [OHS Regs., s. 197(1)]
- The fall arrest system includes a safety strap that prevents the platform from falling more than 15 centimetres, where the personal fall arrest system is attached to the platform. [OHS Regs., s. 197(2)]
- Each personal fall arrest system suspended by a crane is secured to a designated anchorage point on the boom. [OHS Regs., s. 197(3)]
- The operator has an effective means of constant communication with a person on the platform. [OHS Regs., s. 200]
- The installation of a work platform is approved by the manufacturer of a crane. [OHS Regs., s. 198]
- A crane or hoist is not permitted to travel when it is used to suspend: a work platform, except when using a rail-mounted crane. [OHS Regs., s. 199]
Work near high voltage equipment and conductors
Where powered mobile equipment is used, the employer must make sure that a worker does not operate a mobile crane, boom truck, or similar equipment that has the capacity of encroaching on a power line unless they hold a current certification in powerline hazards, obtained from an approved training provider. Powerline hazards training expires after three years. [OHS Regs., s. 483]
When materials, ladders, scaffolds, or other equipment are stored, piled, used, handled, or operated near high voltage equipment and conductors, the employers must: [OHS Regs., s. 498]
- Receive (in writing) the voltage and minimum clearance distance from the power utility before work begins and comply with the work conditions the power utility specifies on the clearance permit.
- Maintain a least 5.5 metres distance from an overhead or underground conductor, if a written clearance is not available from the power utility.
- Get permission from the power utility where a qualified worker must work within the minimum distance using an acceptable work procedure.
The minimum clearance distances are: [OHS Regs., s. 498]
| Voltage Phase to Phase | Minimum Distance |
|---|---|
| Over 750 V to 75 kV | 3 metres |
| Over 75 kV to 250 kV | 4.5 metres |
| Over 250 kV to 550 kV | 6 metres |
Before starting work near high voltage equipment or conductors, the worksite must be inspected by a qualified person who is authorized by the owner of the power system. The purpose of the inspection is to identify hazards, including situations where a part of the tree or equipment may come within the minimum clearance distance from the high voltage equipment or conductor. [OHS Regs., s. 503]
Supervisor Responsibilities
Supervisors must:
- Make all reasonable efforts to protect the health, safety and welfare of the workers under their supervision. [OHS Act, s. 5.1]
- Advise workers under their supervision of present and potential workplace hazards, and provide written or oral instructions about safety precautions that must be followed. [OHS Act, s. 5.2(a)(b)]
- Make sure the workers under their supervision use or wear PPE and safety devices required for their protection. [OHS Act, s. 5.2(c)]
- Take appropriate action when an unsafe condition is reported to them without delay. [OHS Regs., s. 18(2)]
- Make sure a person on an elevating work platform wears a personal fall arrest system secured to an anchorage point that is approved by the manufacturer or professional engineer. [OHS Regs., s. 207(1)]
- Make sure a worker on an aerial ladder is continuously protected by a personal fall arrest system or maintains three points of contact with the ladder at all times. [OHS Regs., s. 207(2)]
- Make sure workers wear high visibility apparel when they are exposed to the danger of contacting moving lift trucks. The high visibility apparel must be suitable for daytime or nighttime, as appropriate. [OHS Regs., s. 81]
- Make sure workers use a personal fall arrest system while working on a work platform mounted on a lift truck. [OHS Regs., s. 217(d)]
- Supervise, or make sure a qualified instructor is overseeing any trainee operating equipment as authorized by the employer. [OHS Regs., s. 252(2)]
- Not knowingly allow a worker to operate mobile equipment which may create undue hazard to the health and safety of a person. [OHS Regs., s. 253]
- Not operate or permit a worker to operate, an elevating work platform that could put the health and safety of a person at risk, or which is in violation of the regulations. [OHS Regs., s 254]
Worker Responsibilities
Workers must:
- Make all reasonable efforts to protect their own health and safety, and that of workers and other persons at, or near, the workplace. [OHS Act, s. 6]
- Cooperate with the employer and co-workers to protect the health and safety of everyone in the workplace. [OHS Act, s. 7(a)]
- Use or wear all necessary PPE and safety devices according to manufacturers’ instructions and training. [OHS Act, s. 7(a.1)] [OHS Regs., s. 17(1)]
- Follow safe work practices and procedures. [OHS Regs., s. 17(2)]
- Immediately report hazards to the supervisor or employer. [OHS Regs., s. 17(3)]
- Cooperate with a person exercising a duty imposed by the OHS Act or Regulations, such as an OHS Officer. [OHS Act, s. 7(c)]
- Not carry out work, or operate a tool, appliance, or equipment, where a present or potential hazard creates imminent danger to themselves or others. [OHS Act, s. 8]
- Not enter or remain at the workplace when impaired by an intoxicating substance or another cause that affects their ability to perform work safely or that may endanger themselves or others. [OHS Regs., s. 26(2)]
- Not stand or pass beneath a suspended load unless no practical alternative exists and a lifting procedure has been communicated to all affected workers. [OHS Regs., s. 318]
The operator of an elevating work platform must:
- Wear high visibility apparel when they are exposed to the danger of contacting moving lift trucks. The high visibility apparel must be suitable for daytime or nighttime, as appropriate. [OHS Regs., s. 81]
- Inspect the elevated work platform before use on each shift, and any condition that could endanger workers must be addressed before the platform may be used. [OHS Regs., s. 205]
- Wear a personal fall arrest system secured to an anchorage point that is approved by the manufacturer or professional engineer, on entry to a platform. [OHS Regs., s. 207(1)]
- Wear a personal fall arrest system or maintain three-point contact with an aerial ladder at all times. [OHS Regs., s. 207(2)]
- Make sure cylindrical objects (e.g., compressed or liquefied gas cylinders, fire extinguishers, etc.) transported on their sides are restrained to prevent unintended movement. [OHS Regs., s. 276]
- Make sure a worker does not stand or pass beneath a suspended load unless no practical alternative exists and a lifting procedure has been communicated to all affected workers. [OHS Regs., s. 318]
Related Topics
Scissor lift
A type of elevating work platform with crisscrossing metal supports that raise and lower the work platform vertically.Personal protective equipment
Any equipment or device which protects a worker's body from injury, illness or death. PPE acts as a barrier to protect the worker from the hazard.PPE should only be used:
- Where other controls are not available or adequate.
- As a short-term measure before controls are implemented.
- During activities such as maintenance, clean up, and repair where other controls are not feasible or effective.
- During emergency situations.
Safe working load (SWL)
The maximum safe force that a piece of lifting equipment, lifting device or accessory can exert to lift, suspend, or lower, a given mass without fear of breaking.Overloading powered mobile equipment can result in the accidental release of the load or the structural or mechanical failure of the lifting equipment. In simple terms, the SWL is the maximum load a piece of equipment can safely lift safely.
The SWL is usually marked on the equipment by the manufacturer.
OHS Officer
An occupational health and safety officer appointed under this Act and includes a medical practitioner providing services under section 20 while he or she is providing those services. [OHS Act, s. 2(i)]Self-propelled
The capability of an elevating work platform to be power propelled with the primary controls on the work platform.Boom-supported elevating work platform
An elevating work platform or aerial device which has its platform supported by an elevating device that elevates and rotates relative to the equipment base.CSA
CSA is the Canadian Standards Association Group. Certain CSA standards are available for online viewing.To access these, you must first create an account with "CSA Communities".
Go to: https://community.csagroup.org/login.jspa?referer=%252Findex.jspa
Once you are logged in, click on the text below the "OHS Standards / View Access" graphic.
Click on the jurisdiction of your choice to see the CSA Standards as referenced in that legislation.
Standards may also be purchased from CSA Group: https://store.csagroup.org/
ANSI
ANSI is the American National Standards Institute.Standards may be purchased from the ANSI store: https://webstore.ansi.org/
OHS Division
Occupational Health and Safety Division, of Digital Government and Service NL regulates occupational health and safety in all provincial workplaces in the province of Newfoundland and Labrador. To date there are approximately 20,000 employers employing about 220,000 workers in the province.
The Division is supported by a complement of staff including OHS officers, industrial hygienists, engineers and radiation specialists to perform various multi-disciplinary activities such as:
- Investigating workplace accidents and statistics
- Conducting compliance inspections and detailed audits of workplaces
- Enforcing Occupational Health and Safety Legislation
https://www.gov.nl.ca/dgsnl/department/branches/divisions/ohs/
Aerial device
A vehicle-mounted device having a boom which may be telescoping or articulating, or both, with a work platform on the boom, which is used to position personnel.Elevating work platform
A vehicle-mounted device having a boom which may be telescoping or articulating, or both, with a work platform on the boom, which is used to position personnel.Aerial ladder
A vehicle-mounted aerial device with a single or multiple-section ladder with or without a platform at the top.Outriggers
A device used to stabilize an elevating work platform.Approved training provider
Some types of training, such as confined space entry, fall protection and power line hazards, must be delivered by WorkplaceNL approved training provider. A list of approved trainers and available courses can be found in the Certification Training Registry (CTR) https://ctr.bluedrop.io/#/OCCUPATIONAL HEALTH AND SAFETY ACT
R.S.N.L. 1990, c. O-3
Section 2 Definitions
2. In this Act
(a) "assistant deputy minister" means an assistant deputy minister appointed under section 9 of the Executive Council Act for the proper conduct of this Act;
(b) "board" means the Labour Relations Board referred to in the Labour Relations Act;
(c) "committee" means an occupational health and safety committee referred to in this Act;
(d) "council" means the Occupational Health and Safety Council referred to in this Act;
(e) "division" means the Occupational Health and Safety Division;
(f) "employer" means a person who employs 1 or more workers;
(g) "minister" means the minister appointed under the Executive Council Act to administer this Act;
(h) "occupation" means employment prescribed by the regulations as an occupation;
(i) "officer" means an occupational health and safety officer appointed under this Act and includes a medical practitioner providing services under section 20 while he or she is providing those services;
(j) "principal contractor" means the person primarily responsible for the carrying out of a project and includes the person who owns the thing in respect of which the project is being carried out;
(k) "self-employed person" means a person who is engaged in an occupation on his or her own behalf;
(k.1) "supervisor" means a person authorized or designated by an employer to exercise direction and control over workers of the employer;
(l) "supplier" means a person who rents or leases tools, appliances or equipment to be used by a worker;
(m) "worker" means a person engaged in an occupation; and
(n) "workplace" means a place where a worker or self-employed person is engaged in an occupation and includes a vehicle or mobile equipment used by a worker in an occupation.
[S.N.L. 1999, c. 28, s. 1; 2006, c. 16, s. 1; 2009, c. 19, s. 1]
Section 4 Employers' general duty
4. An employer shall ensure, where it is reasonably practicable, the health, safety and welfare of his or her workers.
Section 5 Specific duties of employers
5. Without limiting the generality of section 4, an employer
(a) shall, where it is reasonably practicable, provide and maintain a workplace and the necessary equipment, systems and tools that are safe and without risk to the health of his or her workers;
(b) shall, where it is reasonably practicable, provide the information, instruction, training and supervision and facilities that are necessary to ensure the health, safety and welfare of his or her workers;
(c) shall ensure that his or her workers, and particularly his or her supervisors, are made familiar with health or safety hazards that may be met by them in the workplace;
(d) shall, where it is reasonably practicable, conduct his or her undertaking so that persons not in his or her employ are not exposed to health or safety hazards as a result of the undertaking;
(e) shall ensure that his or her workers are given operating instruction in the use of devices and equipment provided for their protection;
(f) shall consult and co-operate with the occupational health and safety committee, the worker health and safety representative or the workplace health and safety designate, where the employer is not the workplace health and safety designate, on all matters respecting occupational health and safety at the workplace;
(f.1) shall respond in writing within 30 days to a recommendation of
(i) the occupational health and safety committee at the workplace,
(ii) the worker health and safety representative at the workplace, or
(iii) where the employer is not the workplace health and safety designate, the workplace health and safety designate at the workplace
indicating that the recommendation has been accepted or that it has been rejected, with a reason for the rejection;
(f.2) shall provide periodic written updates to
(i) the occupational health and safety committee at the workplace,
(ii) the worker health and safety representative at the workplace, or
(iii) where the employer is not the workplace health and safety designate, the workplace health and safety designate at the workplace
on the implementation of a recommendation accepted by the employer until the implementation is complete;
(f.3) shall consult with
(i) the occupational health and safety committee at the workplace,
(ii) the worker health and safety representative at the workplace, or
(iii) where the employer is not the workplace health and safety designate, the workplace health and safety designate at the workplace
about the scheduling of workplace inspections that are required by the regulations, and ensure that the committee, the worker health and safety representative or the workplace health and safety designate participates in the inspection; and
(g) shall co-operate with a person exercising a duty imposed by this Act or regulations.
[S.N.L. 1999, c. 28, s. 2; 2001, c. 10, s. 25; 2004, c. 52, s. 1]
Section 5.1 Supervisors' general duty
5.1 A supervisor shall ensure, where it is reasonably practicable, the health, safety and welfare of all workers under his or her supervision.
[S.N.L. 2009, c. 19, s. 2]
Section 5.2 Specific duties of supervisors
5.2 A supervisor shall
(a) advise workers under his or her supervision of the health or safety hazards that may be met by them in the workplace;
(b) provide proper written or oral instructions regarding precautions to be taken for the protection of all workers under his or her supervision; and
(c) ensure that a worker under his or her supervision uses or wears protective equipment, devices or other apparel that this Act, the regulations or the worker's employer requires to be used or worn.
[S.N.L. 2009, c. 19, s. 2]
Section 6 Workers' general duty
6. A worker, while at work, shall take reasonable care to protect his or her own health and safety and that of workers and other persons at or near the workplace.
Section 7 Specific duties of workers
7. A worker
(a) shall co-operate with his or her employer and with other workers in the workplace to protect
(i) his or her own health and safety,
(ii) the health and safety of other workers engaged in the work of the employer,
(iii) the health and safety of other workers or persons not engaged in the work of the employer but present at or near the workplace;
(a.1) shall use devices and equipment provided for his or her protection in accordance with the instructions for use and training provided with respect to the devices and equipment;
(b) shall consult and co-operate with the occupational health and safety committee, the worker health and safety representative or the workplace health and safety designate at the workplace; and
(c) shall co-operate with a person exercising a duty imposed by this Act or regulations.
[S.N.L. 1999, c. 28, s. 3; 2001, c. 10, s. 26; 2004, c. 52, s. 2]
Section 8 Imminent danger
8. A worker shall not
(a) carry out work where there exists an imminent danger to his or her or another worker's health or safety or the health or safety of another person; or
(b) operate a tool, appliance or equipment that will create an imminent danger to his or her or another worker's health or safety or the health or safety of another person.
Occupational Health and Safety Regulations, 2012
N.L.R. 5/12
Part III GENERAL DUTIES
Section 14 General duties of employers
14. (1) An employer shall ensure, so far as is reasonably practicable, that all buildings, structures, whether permanent or temporary, excavation, machinery, workstations, places of employment and equipment are capable of withstanding the stresses likely to be imposed upon them and of safely performing the functions for which they are used or intended.
(2) An employer shall ensure that necessary protective clothing and devices are used for the health and safety of the employer’s workers.
(3) The employer shall ensure that safe work procedures are followed at all workplaces.
(4) An employer shall ensure, so far as is reasonably practicable, that work procedures promote the safe interaction of workers and their work environment to minimize the potential for injury.
[N.L.R. 43/22, s. 3]
Section 16 Safe working load of equipment
16. (1) Except as provided elsewhere in these regulations, the safe working load of equipment shall be that specified by the manufacturer.
(2) The safe working load of equipment shall be certified by a suitably qualified and registered professional engineer or other person named by the employer and acceptable to the assistant deputy minister where
(a) the manufacturer's specification or other acceptable warranty cannot be produced;
(b) the equipment has been modified in a manner that changes its safe working load;
(c) wear, corrosion, damage or signs of fatigue are found which may reduce the safe working load;
(d) the equipment is used in a manner or for a purpose other than that for which it was originally designed, where that use changes the safe working load; or
(e) the provision of the certification is considered to be necessary by an officer.
Section 17 General duties of workers
17. (1) A worker shall make proper use of all necessary safeguards, protective clothing, safety devices, lifting devices or aids, and appliances
(a) designated and provided for the worker’s protection by the employer; or
(b) required under these regulations to be used or worn by a worker.
(2) A worker shall follow the safe work procedure in which the worker has been instructed.
(3) A worker shall immediately report a hazardous work condition that may come to the worker’s attention to the employer or supervisor.
[N.L.R. 43/22, s. 4]
Section 18 Safety inspections
18. (1) Regular inspections of all buildings, excavations, structures, machinery, equipment, work practices and places of employment shall be made by the employer or the employer’s representative at intervals to ensure that safe working conditions are maintained and that unsafe conditions found as a result of the inspection are remedied without delay.
(2) Where an unsafe condition is discovered by a person, it shall be reported as soon as practicable to a supervisor who shall ensure that appropriate action is taken, without delay, to prevent a worker from being injured.
(3) Where emergency action is required to correct a condition that constitutes an immediate threat to workers, only those qualified and properly instructed workers necessary to correct the unsafe condition shall be exposed to the hazard and every possible effort shall be made to control the hazard while the corrective action is taking place.
[N.L.R. 43/22, s. 5]
Part V GENERAL HEALTH AND SAFETY REQUIREMENTS
Section 26 Personal conduct
26. (1) A worker with a medically documented physical or mental impairment shall not be assigned to work where those impairments endanger the health and safety of that worker or other workers.
(2) An employer, supervisor or worker shall not enter or remain on the premises of a workplace or at a job site while the employer’s, supervisor’s or worker’s ability to perform work responsibilities is impaired by intoxicating substances or another cause that endangers the health or safety of the employer, supervisor or worker or that of other workers.
(3) A person shall not engage in horseplay, scuffling, unnecessary running or jumping, practical jokes or other similar activity or behaviour that may create or constitute a hazard to workers.
(4) Before tools, machinery or equipment is put into operation, the person responsible for doing so shall ensure that all guards are in place and that putting the equipment into operation does not endanger a person.
[N.L.R. 43/22, s. 8]
Section 38 Emergency plan risk assessment
38. (1) An employer shall conduct a risk assessment in a workplace in which a need to rescue or evacuate workers may arise.
(2) Where the risk assessment required by subsection (1) shows a need for evacuation or rescue, appropriate written procedures shall be developed and implemented and a worker assigned to coordinate their implementation.
(3) Written rescue and evacuation procedures are required for but not limited to
(a) work at high angles;
(b) work in confined spaces or where there is a risk of entrapment;
(c) work with hazardous substances;
(d) underground work;
(e) work in close proximity to power lines;
(f) work on or over water; and
(g) workplaces where there are persons who require physical assistance to be moved.
(4) Where a workplace is a low risk workplace in the opinion of an employer, the employer shall post information about escape routes and conduct emergency drills the employer considers appropriate.
[N.L.R. 43/22, s. 10]
Part VII PERSONAL PROTECTIVE EQUIPMENT
Section 72 Instruction
72. An employer shall ensure that a worker who wears personal protective equipment is adequately instructed in the correct use, limitations and assigned maintenance duties for the equipment to be used.
Section 81 High visibility apparel
81. A worker whose duties are regularly performed in areas and under circumstances where the worker is exposed to the danger of moving vehicles or heavy equipment shall wear distinguishing apparel containing highly visible material suitable for daytime or night time use, as appropriate.
[N.L.R. 43/22, s. 17]
Part VIII MACHINERY AND EQUIPMENT
Section 88 Safe machinery and equipment
88. (1) An employer shall ensure that each tool, machine and piece of equipment in the workplace is
(a) capable of safely performing the functions for which it is used; and
(b) selected, used and operated in accordance with
(i) the manufacturer's recommendations and instructions, where available,
(ii) safe work practices, and
(iii) the requirements of these regulations.
(2) Except as otherwise provided in these regulations, the installation, inspection, testing, repair, maintenance or modification of a tool, machine or piece of equipment shall be carried out
(a) in accordance with the manufacturer's instructions or a standard acceptable to the minister; or
(b) as specified by a professional engineer.
(3) Where equipment or a structure is dismantled in whole or in part and subsequently reassembled, it shall not be used until completely checked and found to be safe for operation or occupancy.
Part X FALL PROTECTION
Section 139 Training requirement
139. A worker shall not use fall protection equipment after January 1, 2012 unless the worker has completed a training program on fall protection prescribed by the commission.
[N.L.R. 43/22, s. 23]
Part XI SCAFFOLDS, STAGES AND WORK PLATFORMS
Section 197 Fall protection - suspended work platforms
197. (1) An occupant of a work platform suspended from a crane or hoist shall use a personal fall arrest system with a shock absorbing lanyard secured to a designated anchorage point on the platform or above the load hook.
(2 )Where a work platform suspended by a crane or hoist is occupied by a worker with a personal fall arrest system attached to the platform, the platform shall have a safety strap that prevents the platform from falling more than 15 centimetres where the platform becomes dislodged from the hook.
(3) Each occupant of a work platform attached to a crane boom shall use a personal fall arrest system secured to a designated anchorage point on the boom.
Section 198 Articulating booms prohibited
198. A work platform shall not be
(a) suspended from an articulating boom crane; or
(b) attached to an articulating boom crane unless the installation is approved by the crane manufacturer.
Section 199 Travelling restriction
199. Travelling with a worker in a work platform supported by a crane or hoist is not permitted except where the platform is supported by a rail-mounted crane.
Section 200 Communications
200. The operator of a crane or hoist used to suspend a work platform shall have an effective means of constant communication with a person on the platform.
Section 202 Standards
202. (1) A self-propelled work platform comprising a boom-supported elevating platform, which telescopes, articulates, rotates or extends beyond the base dimensions, and is not mounted on a separate self-propelled vehicle shall meet the requirements of
(a) CSA Standard CAN/CSA-B354.4 "Self-propelled Boom-Supported Elevating Work Platforms" ;
(b) ANSI Standard ANSI/SIA A92.5 "Boom-Supported Elevating Work Platforms"; or
(c) other standard acceptable to the minister.
(2) A self-propelled integral chassis elevating work platform having a platform that cannot be positioned laterally completely beyond the base and for which primary functions are controlled from the platform shall meet the requirements of
(a) CSA Standard CAN/CSA-B354.2 "Self-Propelled Elevating Work Platforms" ;
(b) ANSI Standard ANSI/SIA A92.6 "American National Standard for Self-Propelled Elevating Work Platforms"; or
(c) other standard acceptable to the minister.
(3) A manually propelled, integral chassis elevating work platform having a platform that cannot be positioned laterally completely beyond the base, which may be adjusted by manual or powered means and which shall not be occupied when moved horizontally, shall meet the requirements of
(a) CSA Standard CAN/CSA-B354.1 "Portable Elevating Work Platforms" ;
(b) ANSI Standard ANSI/SIA A92.3 "American National Standard for Manually Propelled Elevating Aerial Platforms"; or
(c) other standard acceptable to the minister.
(4) A telescopic aerial device, aerial ladder, articulating aerial device, vertical tower, material-lifting aerial device or a combination of these, when vehicle-mounted, whether powered or manually operated, shall meet the requirements of CSA Standard CAN/CSA-C225 "Vehicle-Mounted Aerial Devices" or other standard acceptable to the minister.
(5) An elevating work platform of a type other than that referred to in subsections (1) to (4) shall meet a standard acceptable to the minister.
Section 203 Operating and maintenance manuals
203. (1) The equipment manufacturer's
(a) operation manual; and
(b) maintenance manual, containing maintenance instructions and replacement part information
for each elevating work platform in use at the workplace shall be available at the workplace.
(2) Where either of the manuals referred to in subsection (1) is not available, the equipment shall not be used until the manual is obtained, or until written instructions for the safe operation and maintenance of the equipment are supplied by a professional engineer.
Section 204 Inspection and maintenance records
204. (1) Records of inspection, maintenance, repair and modification shall be kept for an elevating work platform by the equipment operator and a person inspecting and maintaining the equipment.
(2) Where the inspection and maintenance records required under subsection (1) are not available, an elevating work platform shall be inspected and certified by a professional engineer before use, and an inspection and maintenance recording system shall be established as required by subsection (1).
Section 205 Shift inspection
205. An elevating work platform shall be inspected by the operator before use on each shift and a condition that could endanger workers shall be remedied before the platform may be used.
Section 206 Annual inspection and certification
206. (1) An elevating work platform shall be inspected, maintained, repaired and modified in accordance with
(a) the manufacturer's instructions;
(b) the relevant CSA Standard as specified in section 202;
(c) the direction of a professional engineer; or
(d) another standard acceptable to the minister.
(2) An insulated aerial device shall be dielectrically tested at least annually in accordance with CSA Standard CAN/CSA-C225 "Vehicle Mounted Aerial Devices" or other standard acceptable to the minister and the insulating capability of the aerial device shall be certified by the testing agency.
Section 207 Fall protection - elevating work platform
207. (1) A person on an elevating work platform shall wear a personal fall arrest system secured to an anchorage point that is approved by the manufacturer or professional engineer.
(2 )A worker on an aerial ladder shall be continuously protected by means of a personal fall arrest system as required by Part X or shall maintain 3 points of contact with the ladder at all times.
Section 208 Safe access
208. Safe means shall be provided to get on and off the platform of an elevating work platform.
Section 209 Rated capacity
209. The rated capacity of an elevating work platform
(a) shall be marked on the platform; and
(b) shall not be exceeded.
Section 210 Outriggers
210. (1) An outrigger on an elevating work platform shall be used in accordance with the manufacturer's instructions.
(2) Where an elevating work platform has outriggers, notices indicating the circumstances specified by the manufacturer for which the outriggers are to be used shall be clearly displayed at the operating controls for the platform.
Section 211 Controls
211. (1) Each control on an elevating work platform shall be clearly identified to indicate its function.
(2) Controls on an elevating work platform shall be 'hold-to-run' (continuous pressure) type that return to the neutral or stop position when released.
(3) Controls on an elevating work platform shall be protected against inadvertent operation.
(4) Each set of operating controls of an elevating work platform shall be provided with an emergency stop device.
(5) An emergency stop device referred to in subsection (4) shall be
(a) within easy reach of the operator;
(b) clearly labelled 'STOP'; and
(c) red in colour.
(6) An elevating work platform shall have a clearly marked overriding lowering control to enable a worker at the lower controls to stop and lower the platform in the event of an emergency.
Section 212 Immobilization of vehicles
212. (1) The carrier vehicle of an elevating work platform shall be secured against inadvertent movement before a worker occupies the platform.
(2) Where a manufacturer permits an elevating work platform to be elevated on sloping ground, the vehicle's wheels shall be secured according to the manufacturer's instructions and where no instructions have been provided, the wheels shall be chocked.
Section 213 Shear hazard
213. An elevating work platform lifting mechanism which creates a shear hazard to workers shall be adequately guarded or identified with signs, decals or similar markings warning of the hazard.
Section 214 Warning devices
214. An elevating work platform, other than a vehicle-mounted aerial device which complies with the requirements of CSA Standard CAN/CSA-C225 "Vehicle Mounted Aerial Device" , shall have a warning system consisting of an intermittent horn and flashing light which is automatically activated during motion of the work platform.
Section 215 Transporting workers
215. A worker may not be transported on an elevated work platform unless the transport is in accordance with the manufacturer's instructions.
Section 217 Fall protection - lift truck
217. Where a worker is elevated on a work platform supported by a lift truck,
(a) the lift truck operator shall remain at the controls of the lift truck;
(b) the lift truck mast shall be kept vertical;
(c) the lift truck shall not be moved except for minor adjustments necessary to facilitate positioning of the platform; and
(d) a platform occupant shall use a personal fall protection system as required by Part X.
Section 249 Window cleaning
249. A window cleaning operation shall be conducted in accordance with the requirements of CSA Standard CAN/CSA-Z91 "Health and Safety Code for Suspended Equipment Operations" or other standard that the minister may consider appropriate.
Part XII POWERED MOBILE EQUIPMENT
Section 251 Operation and maintenance
251. (1) Mobile equipment shall be maintained in safe operating condition and operation, inspection, repair, maintenance and modification shall be carried out in accordance with the manufacturer's instructions or, in the absence of instructions, as approved by a registered professional engineer.
(2) Servicing, maintenance and repair of mobile equipment shall be done
(a) when the equipment is not in operation; or
(b) when the equipment is in operation, where continued operation is essential to the process and a safe means is provided.
(3) The design, fabrication, use, inspection and maintenance of mobile equipment shall meet the requirements of the following applicable standard or other standards acceptable to the minister:
Table
| Equipment | Applicable Standard |
| Mobile and Locomotive Cranes | CSA Standard Z150 , "Safety Code for Mobile Cranes" |
| Vehicles with Mounted Aerial Devices (except fire-fighting equipment) | CSA Standard C225 "Vehicle-Mounted Aerial Devices" |
| Vehicles with Mounted Aerial Devices (fire fighting equipment) | NFPA 1911 "Standard for Inspection, Maintenance, Testing and Retirement of In-Service Automotive Fire Apparatus, 2007 Edition" |
| Safety and Hazard Warnings | ISO Standard 9244:1995 "Earth moving machinery - safety signs and hazard pictorials - General principles |
| Lift Truck and Associated Operator training | CSA Standard B335 "Safety Standard for Lift Trucks" |
(4) Maintenance and inspection records shall be maintained and made reasonably available to the operator and maintenance personnel during work hours.
(5) Mobile equipment used off maintained roads shall be appropriate and safe for the intended use taking into account factors including the nature of the travel surface and its slope and the activities to be undertaken.
(6) Adequate and approved fire suppression equipment shall be provided where required by the minister.
Section 252 Competency and testing operators
252. (1) A person shall not operate mobile equipment unless the person
(a) has received adequate instruction and has demonstrated to a supervisor or instructor that the person is a competent equipment operator;
(b) has been authorized to operate mobile equipment;
(c) is familiar with the operating instructions for particular equipment before the person attempts to operate it; and
(d) has, where required to operate an air brake equipped vehicle, evidence of successful completion of a course on air brake systems issued by an organization acceptable to the minister.
(2) Subsection (1) does not apply where a trainee operates the equipment under the supervision of a qualified instructor or supervisor as authorized by the employer.
[N.L.R. 43/22, s. 25]
Section 253 Operator's responsibility
253. (1) The operator of mobile equipment shall operate the equipment safely, maintain full control of the equipment, and comply with the laws governing the operation of the equipment.
(2) The operator of mobile equipment shall ensure that a worker is not in close proximity to the swing radius of the equipment while it is in operation.
Section 254 Supervisor's responsibility
254. A supervisor shall not knowingly operate, or permit a worker to operate, mobile equipment which is, or which could create, an undue hazard to the health or safety of a person, or which is in violation of these regulations.
Section 259 Load ratings
259. (1) Mobile equipment designed and used for lifting, hoisting or similar operations shall have a permanently affixed notation, legible and visible to the operator, stating the rated load of the equipment.
(2) A load chart shall be displayed in the operator's cab where the rated load varies with the reach of the equipment.
Section 276 Restraint for cylindrical objects
276. Cylindrical objects transported on their sides shall be effectively restrained against inadvertent movement.
Section 277 Lift truck loads
277. (1) A unitized load transported on a lift truck shall not project a distance greater than half its height above the fork carriage, back rest or back rest extension of the lift truck.
(2) No part of a load comprised of loose objects may project above the fork carriage, back rest or back extension of a lift truck.
(3) A load which could shift during transportation shall be restrained where shifting would result in the instability of the load or the lift truck.
Part XIV CRANES, HOISTS AND OTHER LIFTING EQUIPMENT
Section 318 Loads over work areas
318. (1) An employer shall arrange work to prevent passing a load over workers wherever possible.
(2) A crane or hoist operator shall not pass a load over workers unless no practicable alternative exists and the lifting procedure has been communicated to all affected workers.
(3) A worker shall not stand or pass beneath a suspended load except as permitted under subsection (2).
Part XXVI ELECTRICAL OPERATIONS
Section 483 Powerline hazards training
483. A person shall not operate a mobile crane, boom truck or similar equipment that has the capacity of encroaching on a power line without having first completed a safety training program on power line hazards required by the commission.
Section 498 Minimum clearance - high voltage equipment and conductors
498. (1) A worker shall not cause or permit material to be piled, stored or handled, a scaffold to be erected or dismantled or mobile crane, boom truck or similar equipment to operate in an area where overhead or underground conductors are located that are capable of energizing the material, mobile equipment or it load unless the employer has obtained in writing the voltage and minimum clearance distance required by the power utility.
(2) Where the written clearance referred to in subsection (1) is unavailable from the power utility, a minimum 5.5 metres shall be maintained.
(3) An employer shall ensure that at least the minimum applicable distance specified in the following table is maintained between exposed, energized high voltage electrical equipment and conductors and a worker, work, tool, machine, equipment or material, except as otherwise permitted by this Part or a standard acceptable to the minister:
Table
| Voltage Phase to Phase | Minimum Distance |
| Over 750 V to 75 kV | 3 metres |
| Over 75k V to 250 kV | 4.5 metres |
| Over 250 kV to 550 kV | 6 metres |
(4) An employer shall accurately determine the voltage of energized electrical equipment or conductor and the minimum distance from it required under subsection (3).
Section 503 Tree pruning etc. - preliminary inspection
503. Before commencing tree pruning or felling close to energized high voltage overhead conductors, the worksite shall be inspected by a qualified person, authorized by the owner of the power system, to identify a hazard, including situations where a part of the tree to be pruned or felled is within the applicable minimum distance from an energized conductor specified in subsection 498(3) or may fall within that distance.



