Hazard Recognition, Evaluation and Control

Highlighted words reveal definitions when selected.
In order to eliminate workplace hazards and reduce risk, there must be a process for recognizing them, evaluating the risk they pose and choosing the best method to control them.
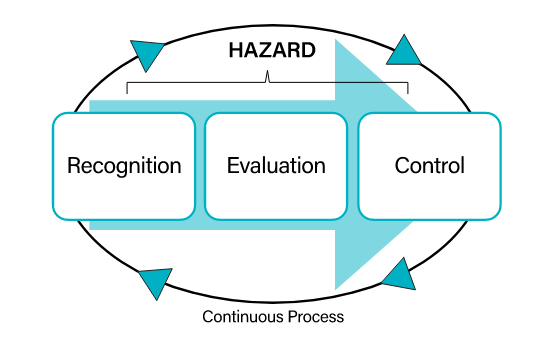
Step 1: Hazard recognition (or identification) - find and record all present and potential hazards in the workplace. Include all work tasks, machinery, equipment, tools, work practices, and conditions; as well as both routine and non-routine events, such as shutdowns, power outages, extreme weather, and emergencies.
Step 2: Evaluation - determine the level of risk posed by a hazard. Thoroughly review all available health and safety information, such as safe work practices and procedures, safety data sheets (SDSs), manufacturer’s instructions, assessment reports, and legislated requirements.
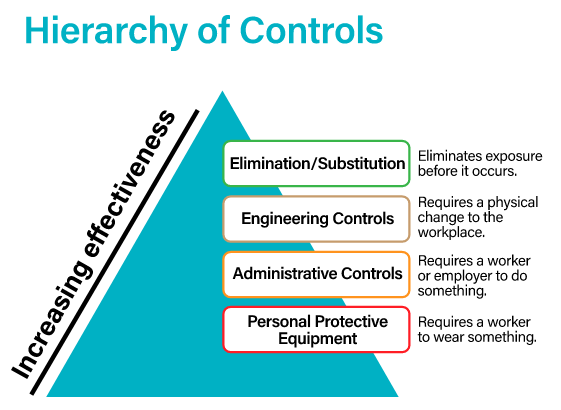
Step 3: Control – reduce the risk of injury or illness happening. The hierarchy of controls establishes that it is best to eliminate or substitute a hazard, where possible, and otherwise reduce the risk using engineering controls or administrative controls.
Personal protective equipment (PPE) is considered to be the least effective method to control a hazard. PPE should only be used when other controls are not practical or adequate, as a short-term measure before controls are implemented, or during emergency situations.
Choose the control(s) specific to the task and include procedures to monitor its effectiveness – this ensures that health and safety in the workplace is maintained and continuously improved.
Employer Responsibilities
Employers must:
- Make all reasonable efforts to protect the health, safety and welfare of their workers. [OHS Act, s. 4]
- Provide and maintain a workplace and the necessary equipment, systems, and tools in a manner that is safe and without risk to workers. [OHS Act, s. 5(a)]
- Provide the necessary information, instruction, training, supervision, and facilities. [OHS Act, s. 5(b)]
- Make sure workers, particularly supervisors, are made familiar with present and potential workplace hazards. [OHS Act, s. 5(c)]
- Conduct business so that people not employed by the employer, such as the public, are not exposed to health or safety hazards created as a result of the work. [OHS Act, s. 5(d)]
- Make sure necessary PPE and devices are used [OHS Regs., s. 14(2)] and workers are given operating instructions for their use. [OHS Act, s. 5(e)]
- Consult and co-operate with the OHS Committee, Workplace Health and Safety Representative, or Designate on all OHS matters. [OHS Act., s. 5(f)]
- Make sure all buildings, structures (both temporary and permanent), excavations, machinery, equipment, workstations, and places of employment:
- Can withstand the stresses likely to be imposed upon them, and can safely perform the function(s) for which they are used or intended. [OHS Regs., s. 14(1)]
- Are inspected regularly to find and correct unsafe working conditions. [OHS Regs., s. 18(1)]
- Make sure that workers follow safe work procedures [OHS Regs., s. 14(3)] that promote the safe interaction of workers and their work environment. [OHS Regs., s. 14(4)]
- Inform all workers and other persons at the workplace of the hazards to which they are likely to be exposed and what controls they must use to protect themselves and others. [OHS Regs., s. 19(1)]
OHS Programs
Employers must have a written OHS Program if they have 10 or more workers at a site [OHS Act, s. 36.1(1)] which includes: [OHS Regs., s. 12(1)(g)]
- Procedures to identify, evaluate, control, and report hazards;
- Procedures and schedules for regular workplace inspections by management and OHS Committee members;
- Procedures for the timely investigation of hazardous events, aimed at finding the root cause and appropriate action(s) to be taken to prevent the event from happening again;
- Policies or procedures to identify when the employer must report hazards to the OHS Committee and how to do this; and
- Procedures to follow, with persons who are responsible, for reporting and correcting hazards.
Supervisor Responsibilities:
Supervisors must:
- Make all reasonable efforts to protect the health, safety and welfare of the workers under their supervision. [OHS Act, s. 5.1]
- Advise workers under their supervision of present and potential workplace hazards, and provide written or oral instructions about safety precautions that must be followed. [OHS Act, s. 5.2(a) and (b)]
- Make sure that the workers under their supervision use or wear PPE and safety devices required for their protection. [OHS Act, s. 5.2(c)]
Workers Responsibilities
Workers must:
- Make all reasonable efforts to protect their own health and safety, and that of workers and other persons at, or near, the workplace. [OHS Act, s. 6]
- Use or wear all necessary PPE and safety devices according to manufacturer’s instructions and training. [OHS Act, s. 7(a.1)] [OHS Regs., s. 17(1)]
- Follow safe work practices and procedures. [OHS Regs., s. 17(2)]
- Immediately report hazards to the supervisor or employer. [OHS Regs., s. 17(3)]
- Not carry out work where a present or potential hazard creates imminent danger to themselves or others. [OHS Act, s. 8(a) and (b)]
- Make sure that all guards are in place and no one will be endangered before starting tools, machinery, or equipment. [OHS Regs., s. 26(4)]
- Participate in training and hazard assessments, where it is offered.
- Not use equipment or perform work tasks where the required training has not yet taken place.
OHS Committee, WHS Representative, and Designate Responsibilities
OHS Committees must:
- Identify aspects of the workplace that may be unhealthy or unsafe. [OHS Act, s. 39(a)]
- Participate in workplace inspections. [OHS Act, s. 39(a.1)]
- Make recommendations to protect the health, safety and welfare of workers at the workplace. [OHS Act, s. 39(b)]
- Receive complaints from workers about their OHS concerns and maintain records of these complaints and any follow-up actions. [OHS Act, s. 39(c) and (e)]
- Establish and promote health and safety educational programs at the workplace. [OHS Act, s. 39(d)]
The Workplace Health and Safety Representative, or Designate must perform the same duties as a Committee, if possible. [OHS Act, s. 44(1)]
Principal Contractor Responsibilities
Principal contractors must:
- Make sure work schedules and tasks are organized to provide safe working conditions for workers. [OHS Regs., s. 19(2)] [OHS Act, s. 10]
- Make sure regulations are followed where a construction project involves the work of two or more employers, and that each employer notifies the principal contractor before starting a task that is likely to create a hazard to a worker of another employer. [OHS Regs., s. 20]
- Designate a person to coordinate the communication of health and safety information at worksites where there are two or more employers working, the combined workforce is more than five workers and the tasks are being done could create a hazard. Where the principal contractor is not at the work location, they must identify a designate. [OHS Regs., s. 21]
Related Topics
Hazard
Any source of potential damage, harm or adverse health effects on something or someone.Hierarchy of controls
The hierarchy, commonly depicted as a triangle, is a hazard control system used to eliminate, or otherwise reduce exposure to hazards.
Eliminate
Elimination removes the hazard. This strategy should be the top priority.
Substitute
Substitution reduces the hazard by replacing it with a less hazardous substitute. For example, a hazardous substance that is normally purchased as a powder could be replaced with a pelleted form that produces less airborne dust during handling.
Engineering controls
Engineering controls remove or reduce the hazard through the design of the workplace, equipment and tools. Common examples include ventilation or enclosing hazardous processes.
Administrative controls
Administrative controls eliminate or reduce exposure to the hazard by employing policies and procedures that reduce risk. Training is an example of an administrative control that increases "workers" knowledge of a hazard.
Personal protective equipment
Any equipment or device which protects a worker's body from injury, illness or death. PPE acts as a barrier to protect the worker from the hazard.PPE should only be used:
- Where other controls are not available or adequate.
- As a short-term measure before controls are implemented.
- During activities such as maintenance, clean up, and repair where other controls are not feasible or effective.
- During emergency situations.
Occupational Health and Safety Committee
Where 10 or more workers are employed at a workplace, the employer shall establish an occupational health and safety committee to monitor the health, safety and welfare of the workers employed at the workplace. [OHS Act, s. 37]A committee shall consist of 2 to 12 persons. Where the employer and workers cannot agree on the size of the committee, the minister may establish its size. [OHS Act, s. 38]
At least half of the members are to be persons representing the workers who are not connected with the management. The persons representing the workers are to be elected by other workers or appointed in accordance with the constitution of the union of which the workers are members.
The employer shall appoint sufficient employer representatives to ensure that the committee may function.
The employer and worker members of a committee shall elect a co-chairperson from their respective groups.
The employer shall post the names of the committee members in a prominent place at the workplace.
A committee:
- Shall seek to identify aspects of the workplace that may be unhealthy or unsafe;
- Shall participate in a workplace inspection that an employer is required by the regulations to conduct;
- May make recommendations to principal contractors, employers, workers, self-employed persons and the Assistant Deputy Minister or an Officer for the enforcement of standards to protect the health, safety and welfare of workers at the workplace;
- Shall receive complaints from workers as to their concerns about the health and safety of the workplace and their welfare;
- Shall establish and promote health and safety educational programs for workers;
- Shall maintain records as to the receipt and disposition of complaints received from workers;
- Shall co-operate with the Assistant Deputy Minister or an Officer who is exercising his or her duties under the act; and
- Shall perform those other duties and follow those procedures that may be prescribed by the regulations. [OHS Act, s. 39]
Worker Health and Safety Representative
Where less than 10 workers are employed at a workplace, the employer shall ensure that a worker not connected with the management of the workplace is designated as the worker health and safety representative to monitor the health, safety and welfare of workers employed at the workplace.[OHS Act, s. 41]
The worker health and safety representative is to be elected by other workers at the workplace or appointed in accordance with the constitution of the labour union of which the workers are members. [OHS Act, s. 42]
The employer shall post the name of the worker health and safety representative in a prominent place at the workplace. [OHS Act, s. 43]
A worker health and safety representative has the same duties as those imposed upon a committee where that is reasonably practicable. [OHS Act, s. 44]
A worker health and safety representative shall consult with his or her employer while performing his or her duties. [OHS Act, s. 44]
OCCUPATIONAL HEALTH AND SAFETY ACT
R.S.N.L. 1990, c. O-3
Section 4 Employers' general duty
4. An employer shall ensure, where it is reasonably practicable, the health, safety and welfare of his or her workers.
Section 5 Specific duties of employers
5. Without limiting the generality of section 4, an employer
(a) shall, where it is reasonably practicable, provide and maintain a workplace and the necessary equipment, systems and tools that are safe and without risk to the health of his or her workers;
(b) shall, where it is reasonably practicable, provide the information, instruction, training and supervision and facilities that are necessary to ensure the health, safety and welfare of his or her workers;
(c) shall ensure that his or her workers, and particularly his or her supervisors, are made familiar with health or safety hazards that may be met by them in the workplace;
(d) shall, where it is reasonably practicable, conduct his or her undertaking so that persons not in his or her employ are not exposed to health or safety hazards as a result of the undertaking;
(e) shall ensure that his or her workers are given operating instruction in the use of devices and equipment provided for their protection;
(f) shall consult and co-operate with the occupational health and safety committee, the worker health and safety representative or the workplace health and safety designate, where the employer is not the workplace health and safety designate, on all matters respecting occupational health and safety at the workplace;
(f.1) shall respond in writing within 30 days to a recommendation of
(i) the occupational health and safety committee at the workplace,
(ii) the worker health and safety representative at the workplace, or
(iii) where the employer is not the workplace health and safety designate, the workplace health and safety designate at the workplace
indicating that the recommendation has been accepted or that it has been rejected, with a reason for the rejection;
(f.2) shall provide periodic written updates to
(i) the occupational health and safety committee at the workplace,
(ii) the worker health and safety representative at the workplace, or
(iii) where the employer is not the workplace health and safety designate, the workplace health and safety designate at the workplace
on the implementation of a recommendation accepted by the employer until the implementation is complete;
(f.3) shall consult with
(i) the occupational health and safety committee at the workplace,
(ii) the worker health and safety representative at the workplace, or
(iii) where the employer is not the workplace health and safety designate, the workplace health and safety designate at the workplace
about the scheduling of workplace inspections that are required by the regulations, and ensure that the committee, the worker health and safety representative or the workplace health and safety designate participates in the inspection; and
(g) shall co-operate with a person exercising a duty imposed by this Act or regulations.
[S.N.L. 1999, c. 28, s. 2; 2001, c. 10, s. 25; 2004, c. 52, s. 1]
Section 5.1 Supervisors' general duty
5.1 A supervisor shall ensure, where it is reasonably practicable, the health, safety and welfare of all workers under his or her supervision.
[S.N.L. 2009, c. 19, s. 2]
Section 5.2 Specific duties of supervisors
5.2 A supervisor shall
(a) advise workers under his or her supervision of the health or safety hazards that may be met by them in the workplace;
(b) provide proper written or oral instructions regarding precautions to be taken for the protection of all workers under his or her supervision; and
(c) ensure that a worker under his or her supervision uses or wears protective equipment, devices or other apparel that this Act, the regulations or the worker's employer requires to be used or worn.
[S.N.L. 2009, c. 19, s. 2]
Section 6 Workers' general duty
6. A worker, while at work, shall take reasonable care to protect his or her own health and safety and that of workers and other persons at or near the workplace.
Section 7 Specific duties of workers
7. A worker
(a) shall co-operate with his or her employer and with other workers in the workplace to protect
(i) his or her own health and safety,
(ii) the health and safety of other workers engaged in the work of the employer,
(iii) the health and safety of other workers or persons not engaged in the work of the employer but present at or near the workplace;
(a.1) shall use devices and equipment provided for his or her protection in accordance with the instructions for use and training provided with respect to the devices and equipment;
(b) shall consult and co-operate with the occupational health and safety committee, the worker health and safety representative or the workplace health and safety designate at the workplace; and
(c) shall co-operate with a person exercising a duty imposed by this Act or regulations.
[S.N.L. 1999, c. 28, s. 3; 2001, c. 10, s. 26; 2004, c. 52, s. 2]
Section 8 Imminent danger
8. A worker shall not
(a) carry out work where there exists an imminent danger to his or her or another worker's health or safety or the health or safety of another person; or
(b) operate a tool, appliance or equipment that will create an imminent danger to his or her or another worker's health or safety or the health or safety of another person.
Section 10 Duty of principal contractor
10. A principal contractor engaged in a project shall ensure, where it is reasonably practicable for him or her to do so, that employers, workers and self-employed persons performing work in respect of that project comply with this Act and the regulations.
Section 36.1 Health and safety program
36.1 (1) Where 10 or more workers are employed at a workplace, the employer shall establish and maintain an occupational health and safety program in accordance with the regulations.
(2) An occupational health and safety program shall be established in consultation with the occupational health and safety committee at the workplace.
(3) An occupational health and safety program shall include those documents that may be prescribed in the regulations.
(4) An occupational health and safety program shall be in writing and shall, when requested, be provided to the occupational health and safety committee, a worker at the workplace and an officer.
[S.N.L. 2001, c. 10, s. 27; 2004, c. 47, s. 27]
Section 37 Committees
37. Where 10 or more workers are employed at a workplace, the employer shall establish an occupational health and safety committee to monitor the health, safety and welfare of the workers employed at the workplace.
[S.N.L. 1999, c. 28, s. 9]
Section 38 Membership of committees
38. (1) A committee shall consist of the number of persons that may be agreed to by the employer and the workers but shall not be less than 2 nor more than 12 persons.
(2) At least half of the members of a committee are to be persons representing the workers at the workplace who are not connected with the management of the workplace.
(3) The persons representing the workers on the committee are to be elected by other workers at the workplace or appointed in accordance with the constitution of the union of which the workers are members.
(4) Where the employer and workers cannot agree on the size of the committee, the minister may establish its size.
(5) The employer shall appoint sufficient employer representatives to ensure that the committee may function.
(6) The employer and worker members of a committee shall elect a co- chairperson from their respective groups.
(7) The employer shall post the names of the committee members in a prominent place at the workplace.
Section 39 Duties of committees
39. A committee established under section 37
(a) shall seek to identify aspects of the workplace that may be unhealthy or unsafe;
(a.1) shall participate in a workplace inspection that an employer is required by the regulations to conduct;
(b) may make recommendations to principal contractors, employers, workers, self-employed persons and the assistant deputy minister or an officer for the enforcement of standards to protect the health, safety and welfare of workers at the workplace;
(c) shall receive complaints from workers as to their concerns about the health and safety of the workplace and their welfare;
(d) shall establish and promote health and safety educational programs for workers;
(e) shall maintain records as to the receipt and disposition of complaints received from workers under paragraph (c);
(f) shall co-operate with the assistant deputy minister or an officer who is exercising his or her duties under the Act; and
(g) shall perform those other duties and follow those procedures that may be prescribed by the regulations.
[S.N.L. 2001, c. 10, s. 29]
Section 40 Meetings of committee
40. Meetings of a committee shall take place during regular working hours at least once every 3 months and a worker is not to suffer loss of pay or other benefits while engaged in a meeting of a committee.
Section 41 Worker representative
41. (1) Where less than 10 workers are employed at a workplace, the employer shall ensure that a worker not connected with the management of the workplace is designated as the worker health and safety representative to monitor the health, safety and welfare of workers employed at the workplace.
(2) The employer shall provide and pay for training for the worker health and safety representative.
(3) The training provided under subsection (2) shall meet the requirements the Workplace Health Safety and Compensation Commission may set.
(4) The worker health and safety representative shall participate in the training provided under this section.
(5) An employer shall compensate a worker for participating in training under this section as if the training were regular work.
[S.N.L. 2001, c. 10, s. 30; 2004, c. 47, s. 27]
Section 42 Election of representative
42. The worker health and safety representative is to be elected by other workers at the workplace or appointed in accordance with the constitution of the labour union of which the workers are members.
Section 43 Posting name
43. The employer shall post the name of the worker health and safety representative or the workplace health and safety designate in a prominent place at the workplace.
[S.N.L. 2004, c. 52, s. 9]
Section 44 Duties of representative
44. (1) A worker health and safety representative or the workplace health and safety designate has the same duties as those imposed upon a committee under section 39, where that is reasonably practicable.
(2) A worker health and safety representative or the workplace health and safety designate, where the workplace health and safety designate is not the employer, shall consult with his or her employer while performing his or her duties under subsection (1).
(3) Where the workplace health and safety designate is the employer, he or she shall consult with the workers while performing his or her duties under subsection (1).
[S.N.L. 2004, c. 52, s. 10]
Occupational Health and Safety Regulations, 2012
N.L.R. 5/12
Part III GENERAL DUTIES
Section 12 Occupational health and safety program
12. (1) An occupational health and safety program required under section 36.1 of the Act shall be signed and dated by the employer and by the person or persons responsible for the management of the employer's operations in the province and shall include:
(a) a statement of the employer's commitment to cooperate with the occupational health and safety committee and workers in the workplace in carrying out their collective responsibility for occupational health and safety;
(b) a statement of the respective responsibilities of the employer, supervisors, the occupational health and safety committee and workers in carrying out their collective responsibility for occupational health and safety;
(c) procedures to identify the need for, and for the preparation of written safe work procedures to implement health and safety practices, including practices required by the Act and the regulations, or as required by an officer;
(d) written work procedures appropriate to the hazards and work activity in the workplace;
(e) a plan for orienting and training workers and supervisors in workplace and job-specific safe work practices, plans, policies and procedures, including emergency response, that are necessary to eliminate, reduce or control hazards;
(f) provisions for establishing and operating an occupational health and safety committee, including provisions respecting
(i) maintenance of membership records,
(ii) procedural rules,
(iii) access by the committee to management staff with the authority to resolve health and safety issues and to information about the employer's operations required under the Act and the regulations, and
(iv) a plan for training committee members as required under the Act;
(g) a system for the recognition, evaluation and control of hazards that includes:
(i) evaluation and monitoring of the workplace to identify potential hazards and the associated risks,
(ii) procedures and schedules for regular inspections by management and committee members,
(iii) procedures for the identification, reporting and control or correction of hazards,
(iv) procedures for the prompt investigation of hazardous occurrences to determine the cause of the occurrence and the actions necessary to prevent a recurrence,
(v) identification of the circumstances where the employer is required to report hazards to the committee and the procedures for doing so, and
(vi) measures for the accountability of persons responsible for the reporting and correction of hazards;
(h) a plan for the control of biological and chemical substances handled, used, stored, produced or disposed of at the workplace and where appropriate, the monitoring of the work environment to ensure the health and safety of workers and other persons at or near the workplace;
(i) a system to ensure that persons contracted by the employer or for the employer's benefit comply with the program developed under this section and the Act and regulations;
(j) an emergency response plan;
(k) maintenance of records and statistics, including occupational health and safety committee minutes, reports of occupational health and safety inspections and investigations, with procedures to allow access to them by persons entitled to receive them under the Act; and
(l) provision for monitoring the implementation and effectiveness of the program.
(2) An employer that is required to establish and maintain an occupational health and safety program under section 36.1 of the Act shall
(a) implement the occupational health and safety program; and
(b) review and, where necessary, revise the occupational health and safety program as follows:
(i) at least every 3 years,
(ii) where there is a change of circumstances that may affect the health and safety of workers, and
(iii) where an officer requests a review.
Section 14 General duties of employers
14. (1) An employer shall ensure, so far as is reasonably practicable, that all buildings, structures, whether permanent or temporary, excavation, machinery, workstations, places of employment and equipment are capable of withstanding the stresses likely to be imposed upon them and of safely performing the functions for which they are used or intended.
(2) An employer shall ensure that necessary protective clothing and devices are used for the health and safety of the employer’s workers.
(3) The employer shall ensure that safe work procedures are followed at all workplaces.
(4) An employer shall ensure, so far as is reasonably practicable, that work procedures promote the safe interaction of workers and their work environment to minimize the potential for injury.
[N.L.R. 43/22, s. 3]
Section 17 General duties of workers
17. (1) A worker shall make proper use of all necessary safeguards, protective clothing, safety devices, lifting devices or aids, and appliances
(a) designated and provided for the worker’s protection by the employer; or
(b) required under these regulations to be used or worn by a worker.
(2) A worker shall follow the safe work procedure in which the worker has been instructed.
(3) A worker shall immediately report a hazardous work condition that may come to the worker’s attention to the employer or supervisor.
[N.L.R. 43/22, s. 4]
Section 18 Safety inspections
18. (1) Regular inspections of all buildings, excavations, structures, machinery, equipment, work practices and places of employment shall be made by the employer or the employer’s representative at intervals to ensure that safe working conditions are maintained and that unsafe conditions found as a result of the inspection are remedied without delay.
(2) Where an unsafe condition is discovered by a person, it shall be reported as soon as practicable to a supervisor who shall ensure that appropriate action is taken, without delay, to prevent a worker from being injured.
(3) Where emergency action is required to correct a condition that constitutes an immediate threat to workers, only those qualified and properly instructed workers necessary to correct the unsafe condition shall be exposed to the hazard and every possible effort shall be made to control the hazard while the corrective action is taking place.
[N.L.R. 43/22, s. 5]
Section 19 Co-ordination of work
19. (1) An owner shall ensure that all workers and other persons at the workplace are informed of
(a) the hazards of an owner's operations or site conditions; and
(b) the health and safety activities to be used to address the hazards.
(2) A principal contractor shall ensure work schedules and tasks are organized to provide safe working conditions for workers.
Section 20 Two or more employers
20. Where a construction project involves the work of 2 or more employers or their workers,
(a) the principal contractor shall ensure compliance with the regulations where conditions or activities affect the workers of more than one employer; and
(b) each employer shall notify the principal contractor in advance of an undertaking likely to create a hazard for a worker of another employer.
Section 21 Appointment of qualified co-ordinator
21. Where, at a work location, the overlapping or adjoining work activities of 2 or more employers create a hazard to workers and the combined work force at the workplace is more than 5 persons, the principal contractor shall
(a) ensure that an individual is designated at the work location to coordinate communication for the purpose of ensuring health and safety on the worksite; and
(b) where the principal contractor is not at the work location the principal contractor shall designate a person to assume the duty.
Part V GENERAL HEALTH AND SAFETY REQUIREMENTS
Section 26 Personal conduct
26. (1) A worker with a medically documented physical or mental impairment shall not be assigned to work where those impairments endanger the health and safety of that worker or other workers.
(2) An employer, supervisor or worker shall not enter or remain on the premises of a workplace or at a job site while the employer’s, supervisor’s or worker’s ability to perform work responsibilities is impaired by intoxicating substances or another cause that endangers the health or safety of the employer, supervisor or worker or that of other workers.
(3) A person shall not engage in horseplay, scuffling, unnecessary running or jumping, practical jokes or other similar activity or behaviour that may create or constitute a hazard to workers.
(4) Before tools, machinery or equipment is put into operation, the person responsible for doing so shall ensure that all guards are in place and that putting the equipment into operation does not endanger a person.
[N.L.R. 43/22, s. 8]
CCOHS



